NFC is an acronym for Near Field Communication, and it’s often used when referring to modern smartphones and tablets. What does NFC mean, and what does NFC do? Many people buy expensive smartphones, which all have NFC on them, but they have no idea what NFC is or how they can use it. If you would like to learn more about NFC, NFC-enabled devices, NFC tags, and NFC readers, read on:
What is NFC? What does NFC mean?
NFC stands for Near Field Communication, and, essentially, it’s a set of close-range, low-power wireless communication standards. NFC allows electronic devices to establish two-way radio communication with each other, using complementary technologies such as Bluetooth or WiFi. NFC is a wireless technology that will work within a few centimeters of another NFC-enabled device.
How does NFC work?
NFC works by touching two devices or placing them close to each other at distances that are less than 4 inches or 10 centimeters.
You have probably heard about RFID or Radio-Frequency Identification. The most widespread use of RFID tags is in credit cards. If your credit card supports contactless payment, that’s because it has an RFID tag in it, and retail stores can read the information on it to charge you.
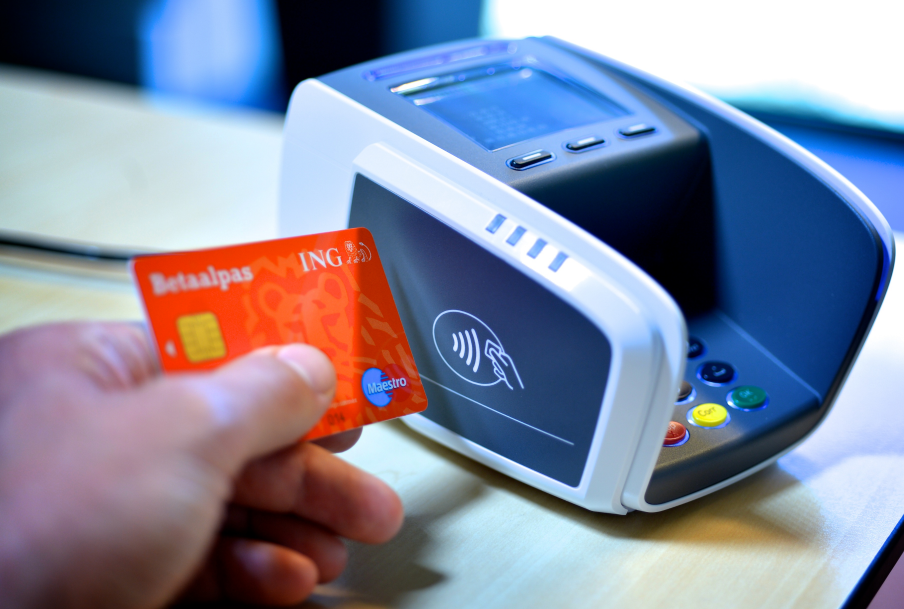

Contactless card with RFID. Photo by ING Nederlands
NFC is a technology similar to RFID, but with the crucial difference that, while RFID chips can only be read, NFC also lets your device transmit and receive information from other NFC-enabled devices. Therefore, while NFC and RFID are similar, they are not the same thing.
When you pair two NFC-enabled devices, NFC can automatically connect them using Bluetooth and then start transferring information between them. Some devices, like Samsung Galaxy smartphones, can also use NFC to initiate a Direct WiFi connection between your devices automatically. Compared to Bluetooth, WiFi Direct is much faster.
What does NFC do on my phone?
NFC has many uses, and the most common are the following:
- Transfer contacts and web pages between your smartphones - instant transfer of contacts and web pages between smartphones with NFC. It is a quick way to transfer such data between two smartphones.
- Contactless payments with your smartphone - you can use your NFC-enabled smartphone to perform quick payments, just like you would with a credit card. Both Google and Apple provide NFC payment solutions through their mobile Wallet apps. In these apps, you can store your credit card information and then make payments with your smartphone instead of your credit card. The payment process is thus faster.
- Pair your smartphone with other consumer electronic devices - NFC can be used to pair your iPhone or your Android smartphones with headsets, portable speakers, media players, or game controllers that also have NFC.
- Pair your smartphone with your car - NFC is also getting great adoption from car manufacturers because this technology can allow users to connect their smart devices to their car multimedia system quickly. Companies such as BMW or Mercedes have added NFC to their new car models.
- Transfer files from or to your smartphone - NFC can be used to automatically complete the steps of enabling, pairing, and establishing Bluetooth or Direct WiFi connections to perform file transfers between two NFC-enabled smartphones, but also from your smartphone to your tablet, laptop, or 2-in-1 device.
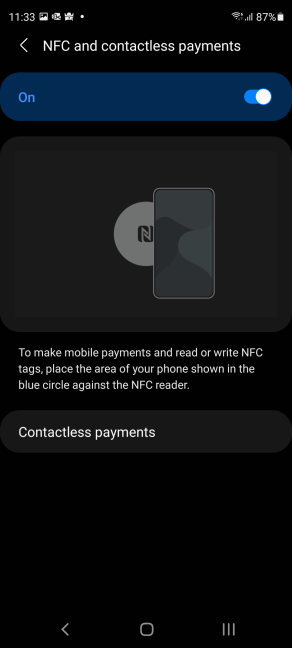
Enabling NFC and contactless payments on a Samsung Galaxy
What is an NFC tag?
NFC tags are small, inexpensive, smart tags made with a tiny amount of storage memory, a radio chip, and a small antenna. They are very thin devices that can be inserted into small plastic cases or even stuck to a paper or a flyer. NFC tags don’t need batteries to run: they draw their power from NFC-enabled devices that you tap or keep close to them using induction.

A smart NFC tag made by Samsung (Galaxy Smart Tag)
What is an NFC tag reader?
NFC tags can be read with, you guessed, an NFC tag reader. NFC tag readers are NFC-enabled devices that can read the information stored on an NFC tag. The most common NFC readers are smartphones. Usually, Android devices can read (and also write) NFC tags by default, as the operating system knows how to work with this technology. On the other hand, only newer iPhones can do that directly, as Apple didn’t use to let iOS automatically read NFC tags on older iPhones. We’re touching on this subject in more detail later in this article.
Where else is NFC used?
There are also other uses that are not widespread at this point but are made available by some companies. One of the most interesting is that NFC can be used for access and security checks: you can use NFC devices, such as your smartphone, to validate your identity and get access to your office building, for example. Several companies and universities are also using NFC-enabled devices as security badges. Also, companies like Iberia airlines in Spain allow travelers to store their boarding passes on their NFC-enabled phones. Similarly, the Scottish railway operator Rambus lets you pay for your train tickets using NFC-enabled smartphones.

NFC reader in a public transport vehicle
Is NFC dangerous? Should NFC be on or off?
The only major downside of this technology is that it does not provide any security or protection outside the fact that communication can be done only within a very close range (of a few inches or centimeters). NFC is vulnerable to all kinds of attacks, from eavesdropping to data modification. A complete list of vulnerabilities was documented on Wikipedia: NFC Vulnerabilities. So, while NFC is not dangerous by itself, we do recommend you to keep it off and only enable NFC when you need it.
Do I have NFC on my Android smartphone?
Not all Android smartphones have NFC available, at least not the cheaper models. To tell whether you have NFC on your Android smartphone, first open the Settings. Then, use the search field to look for NFC. It is usually found in the Wireless & networks category (or the Connections category on Samsung Galaxy smartphones), somewhere beneath Bluetooth, or in a More connections section. If you get a search result named NFC, then you have NFC on your smartphone. Tap on the NFC search result and, on the next screen, turn the NFC switch on to enable it.
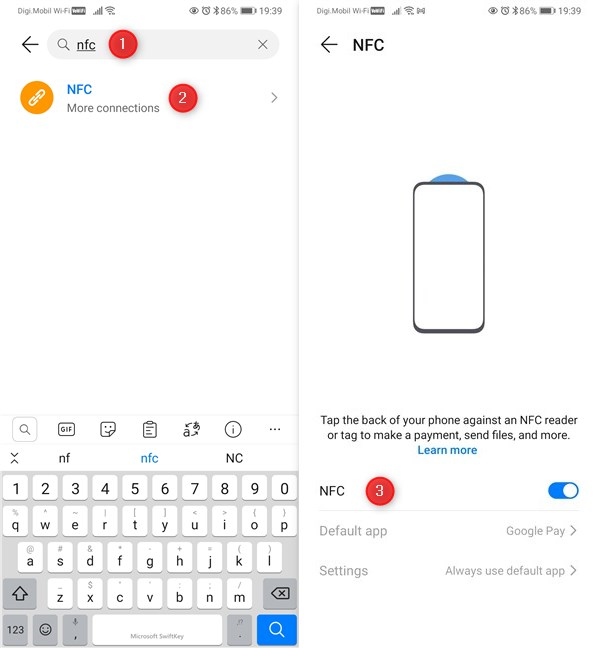
Enabling NFC on an Android smartphone
If you want to know more, learn how to enable and use NFC on Android.
Do I have NFC on my iPhone?
Many iPhones do have NFC, but some of them don’t, and some just can’t use all the benefits of NFC because Apple chose not to include all its features on its smartphones:
- If you have an iPhone 5, 5s, 5c, or previous, you do not have NFC;
- If you have an iPhone 6, 6 Plus, or iPhone SE, you have NFC but only for payments, using Apple Pay;
- If you have an iPhone 7, iPhone 8, iPhone X, iPhone SE 2nd Gen, iPhone 11, or iPhone 12, you have NFC for payments, and you can also read NFC tags, but only if you are using iOS 11 or newer. If you have iOS 14 or newer, you can also write NFC tags using third-party apps.

An iPhone (SE 2nd Gen) that has NFC
Follow this link to get more detailed information about iPhones’ NFC.
Final words: Who made NFC and when?
Sony, Philips, and Nokia invented this technology. The first phone with NFC was Nokia 6131, and it was released in 2006. The first Android smartphone with NFC was the Nexus S, and it was released in 2010.
Hundreds of companies have now adopted this technology, and it is widely used in all kinds of devices like smartphones, tablets, PCs, portable speakers, and even cars. The evolution of this technology and its standard is managed by the NFC Forum - a non-profit industry association. This forum has more than 100 members, and it includes most of the prominent companies in the world of technology, including Intel, Microsoft, and Google. All the major mobile manufacturers are also members.
How do you use NFC?
As you can see, NFC is a promising technology that can be used for many things. Its growing adoption in all kinds of mobile devices, especially smartphones, will only increase its importance in the future. Are you using NFC to send data between your smartphones, connect to your portable speakers, or other tasks? Did you get to our guide simply because you got a “what is NFC?” MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) on an exam? Let us know, and share your experience with NFC, as well as any questions you might have about NFC, in the comments section below.