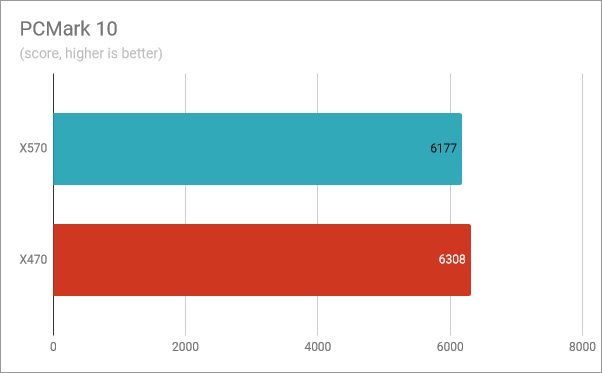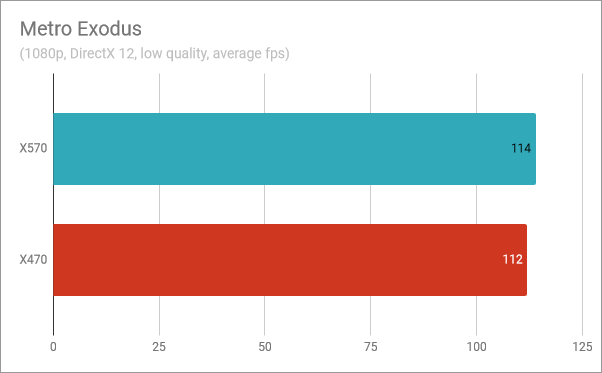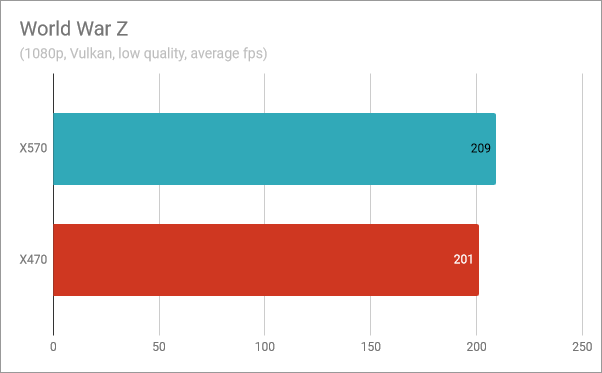Do you love the new processors from AMD Ryzen 3000 series? You already have a desktop PC with a Ryzen processor, and you want to know whether you should also buy a new motherboard alongside your new processor? If you have a motherboard with the previous X470 chipset, here is a detailed performance comparison against the newer X570 chipset for the AMD Ryzen 3000 processors. We used the AMD Ryzen 5 3600X processor to run several tests and benchmarks on motherboards with these two chipsets. Our goal was to see if buying a new motherboard brings meaningful performance differences vs. the previous generation of motherboards for AMD Ryzen processors. Here is what we found:
Do the new AMD Ryzen 3000 processors work on older motherboards with X470 and x370 chipsets?
AMD has a great history of keeping its different generations of processors compatible with its motherboard chipsets for long periods. That is also true about the third generation of Ryzen processors that was recently launched. All the Ryzen 3000 processors use the same Socket AM4 for motherboards. They are also compatible not only with the latest X570 chipset motherboards, but also with older motherboards, using the previous X470 and X370 chipsets, as well as with some of the more budget-oriented B450 and B350 mainboards.
However, to be able to use a Ryzen 3000 CPU on an older motherboard, you have to update its BIOS to support the new processor. Most motherboard manufacturers should have already released new BIOS versions. It all depends on the motherboard vendors and whether they bothered to update the BIOS for the specific motherboard that you own.
You can find out more about the compatibility between motherboards and the new Ryzen 3000 processors, on this page: Socket AM4 X570 Motherboards. Also, a passionate user has made this long spreadsheet with plenty of useful details about this subject: Motherboards chart compatibility for Ryzen 3000.
What is the difference between the X570 and X470 motherboard chipsets?
In this article, we are focusing on the high-end X570 and X470 chipsets for AMD Ryzen processors. At launch, the X570 chipset is the only one in the world that offers the new PCI Express 4 technology. None of the previous AMD motherboard chipsets, including the X470, nor any of the Intel chipsets, provide PCI Express 4.
The AMD Ryzen 3000s processors have a total number of twenty-four PCI Express 4 lanes:
- 16 lanes for the graphics card
- 4 lanes that offer increased bandwidth between the processor and the motherboard chipset
- 4 lanes for fast storage devices such as NVMe solid-state drives.
The X570 chipset offers another sixteen PCIe 4 lanes that the manufacturers can use as they wish for other hardware components and interfaces. For example, they could use up to two NVMe solid-state drives or eight SATA 6Gb/s hard disk drives.
Then, the other essential improvements in the X570 chipset versus the older X470, are better VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) for the processor, and a better wiring specification for the RAM. This means more power is going to the processor and RAM, and users receive better stability and more overclocking possibilities than before.
Last but not least, the X570 chipset also offers eight USB 3.0 Gen 2 ports with speeds of up to 10 Gbps, and four USB 2.0 ports. In comparison, the X470 has only two USB 3.2 Gen2 ports, six USB 3.2 Gen 1 ports, and six USB 2.0 ports.
Unfortunately, all of the above come with increased energy requirements for the X570 chipset compared to the older X470 chipset. The new chipset needs more power to run: it has a TDP of about 15 watts, while the X470 chipset has a TDP of only 5 watts. That is why most of the X570-based motherboards come with a dedicated fan on them, which some users do not like. In the future, maybe we are going to also see X570 motherboards with heat pipes instead of fans on them.
Benchmarking the AMD Ryzen 5 3600X with X570 vs. AMD Ryzen 5 3600X with X470
To see whether there are differences in terms of performance when using X570 chipset motherboards vs. older X470 chipset motherboards, we built a test PC of our own. It had the new AMD Ryzen 5 3600X processor and with the following hardware:
- Motherboard: ASUS ROG Crosshair VIII Hero (Wi-Fi) and ASUS ROG Crosshair VII Hero (Wi-Fi)
- Memory: HyperX Predator DDR4 RGB Memory (2 x 8GB, 3600MHz)
- Graphics Card: ASUS ROG STRIX GTX 1660 Ti GAMING OC
- Storage: ADATA XPG Gammix S11 Pro SSD
- Monitor: ASUS ROG Strix XG32VQ Curved Gaming Monitor (32-inch WQHD 2560 x 1440, 144Hz)
- Power Supply Unit: ASUS ROG Thor 850W Platinum
- Operating System: Windows 10 Pro x64 with May 2019 Update
The only component that we changed was the motherboard. To make the best possible comparison, we used different iterations of the same motherboard: ASUS ROG Crosshair VII Hero (Wi-Fi) with an older X470 chipset, and ASUS ROG Crosshair VIII Hero (Wi-Fi) with the new X570 chipset.
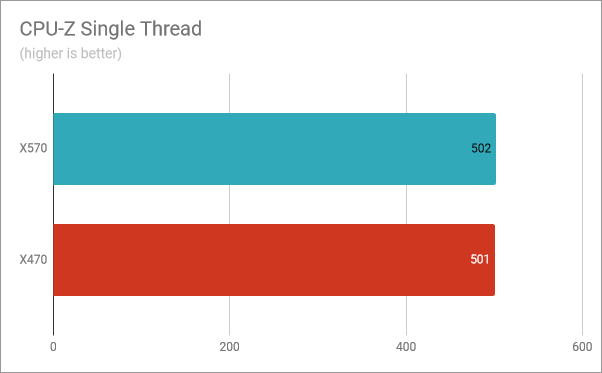
We started with the CPU-Z Single Thread benchmark, which tests the single-core performance offered by the processor. We got a score of 502 using the X570 motherboard and a score of 501 on the X470 motherboard. This tiny difference is insignificant, meaning that the single-core speed of the processor, on both motherboard chipsets, is the same.
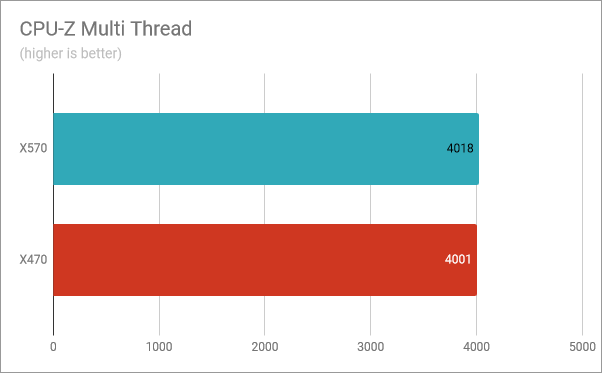
CPU-Z also has a Multi-Thread benchmark which tests the speed of the processor when using all its cores. When using the X570 motherboard, the AMD Ryzen 5 3600X got a score of 4018 points, while on the X470 mainboard, it got 4001. The performance difference is less than 0.5%.
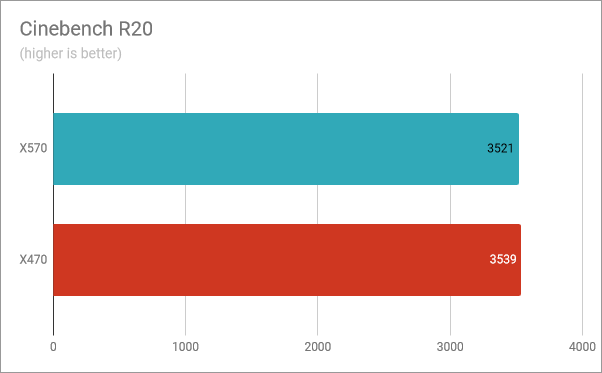
Next, we turned to the Cinebench R20 benchmark, which evaluates the processor speed when rendering. The results were again similar, although the X470 chipset had a slightly better result. However, the difference between the two chipsets is just 0.5 percent.
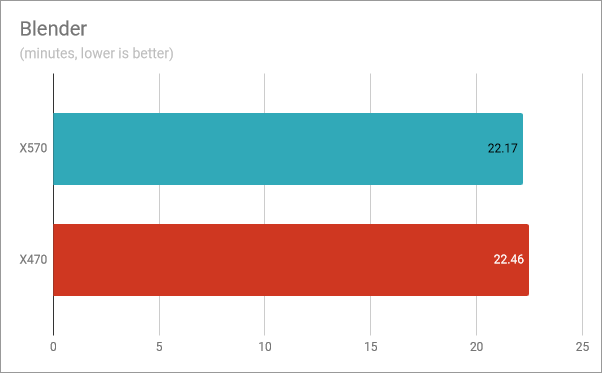
In the Blender benchmark, which evaluates the processor's speed by rendering two different scenes and measuring the time of completion, using the AMD Ryzen 5 3600X with the X570 motherboard was faster by 17.4 seconds. It looks like using the X570 chipset is marginally quicker than using the X470 chipset. Still, a rather insignificant difference.
PCMark 10 benchmarks the computer's performance in daily activities. By that, we understand web browsing, video conferencing, apps start-up times, productivity, and digital content creation. Interestingly, the AMD Ryzen 5 3600X processor with the X570 chipset had a slightly lower score than with the X470 chipset, by about two percent. Again, a tiny difference.
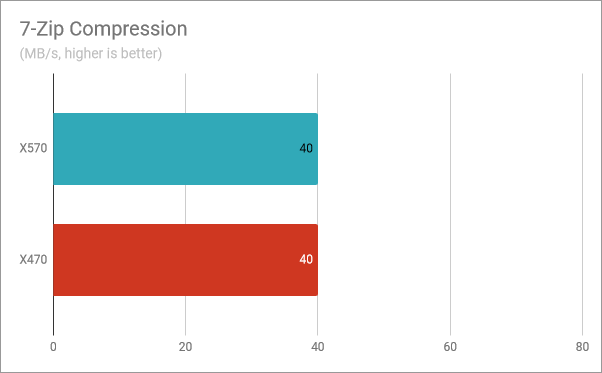
7-Zip is a very popular file compression program, and it is also great at assessing the speed of computer processors. When we benchmarked the Ryzen 5 3600X, we got the same compression speed of 40 MB/s regardless of the motherboard chipset that we used.
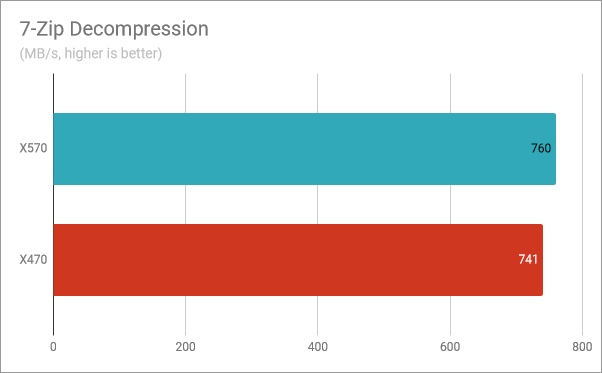
In the decompression test, the Ryzen 5 3600X processor was slightly faster with the X570 motherboard than it was with the X470 motherboard. The difference between the two chipsets was of 2.5%.
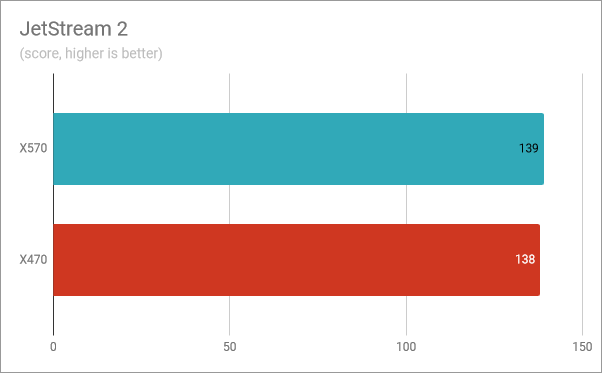
JetStream 2 is a benchmark designed to measure the web browsing performance. Using Google Chrome, we got almost the same score on both chipsets. This confirms that, when it comes to browsing the web, the AMD Ryzen 5 3600X runs just as fast on motherboards with the X570 chipset as it does on those with X470.
We also checked a few games. For each of them, we used the 1080p resolution and the lowest graphic details available, so that the video card does not bottleneck the processor.
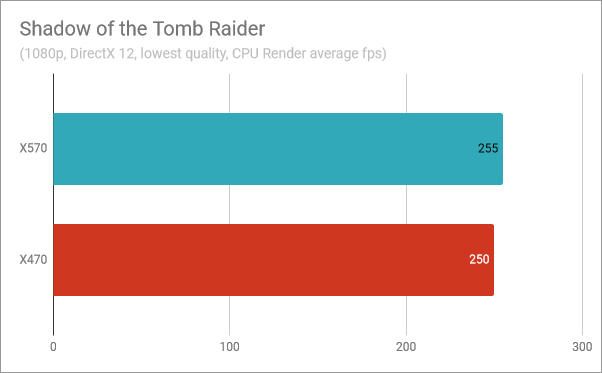
In Shadow of the Tomb Raider, the CPU Render measurements showed that we got five frames per second more on the X570 chipset than on the X470 chipset. It is a small improvement of just 2%.
Metro Exodus showed a similar result: 114 FPS on the X570 chipset versus 112 frames with the X470 chipset. The performance difference is only 1.75%.
On World War Z, a game with zombies, that can use the Vulkan API, we measured 8 FPS more with the X570 chipset than with the X470. However, on both chipsets, we got over 200 frames per second, which means that the 8 FPS difference represents just 3.8%.
Our tests have shown that the AMD Ryzen 5 3600X processor is just as fast if you use it on a motherboard with an X570 chipset as it is on a motherboard with an X470 chipset. The performance differences are insignificant, varying from 0 to 3.8%.
When upgrading to an AMD Ryzen 3000 processor should you ditch your previous X470 motherboard?
If you have a desktop PC with an older motherboard with the X470 chipset, there is no reason to buy a new motherboard with the new X570 chipset. Only buy a new processor from the Ryzen 3000 series, and keep your existing hardware. You won't notice meaningful performance differences, if you also buy a new motherboard with the X570 chipset. A processor like AMD Ryzen 5 3600X offers excellent performance on motherboards with the X470 chipset too.
When does it make sense to invest in an X570 motherboard?
Investing in a motherboard with the X570 chipset makes sense if:
- You do not mind the premium price you have to pay for motherboards with this chipset
- You want your PC to be future-proof, and use PCI Express 4 video cards like AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT, and NVMe SSD drives.
- You long for an abundance of USB 3.2 Gen 2 ports
- You are building a new PC instead of upgrading an older one with a previous generation Ryzen processor
- The prices for motherboards with the X570 chipset decrease and motherboards with the X470 chipset begin to get phased out from the market
Do you plan to switch to the Ryzen 3000 series of processors?
At the end of this performance comparison, we would like to know whether you plan to buy an AMD Ryzen 3000 series processor and switch to this promising platform. If you do, which motherboard do you consider buying? Is it one with an X570 chipset or a cheaper one with an X470 chipset? Comment below and share your perspective.