When you look for a new computer processor to buy, you stumble upon technicalities such as CPU base clock or CPU boost speed. Did you wonder what that means? While all processors have a base clock (operating frequency) that is in the range of a few Gigahertz, modern processors also advertise higher turbo boost speeds. Whether you're looking into AMD or Intel processors, all of them show off with their turbo boost clocks. Here is what Turbo Boost means when it comes to processors:
What is the processor base clock?
You should first understand what the processor (CPU - Central Processing Unit) base clock is. The base clock is a processor's standard speed or operating frequency. It is measured in Gigahertz, and tells you how many billions of calculations it can perform in one second.
In the early days of computers, processors only ran at their base clock (frequency), which meant that they had a fixed speed, that did not go up or down. It also meant that comparing processors to find out which was faster was fairly easy. In general, a processor with a higher clock was faster than a processor with a lower clock. For example, a 3 GHz processor was faster than a 2.5 GHz processor, although other things such as processor architecture or the amount Cache memory could alter the balance.
What is the processor turbo boost clock?
Modern processors, however, also have a second turbo boost clock, that complicates things a bit. What does the turbo boost clock mean? Well, both AMD and Intel nowadays create computer processors that can adjust their speed depending on what you are doing. The turbo boost clock is the maximum speed at which a processor can run.
You can say that processors that can turbo boost, overclock themselves, without your intervention. For example, a processor that has a standard base frequency of 3.6 GHz and a turbo boost clock of 4.6 GHz, such as the Ryzen 7 3700X, can run at 4.6 GHz when you are running demanding apps or games, but only runs at 3.6 GHz in the rest of the time. The processor handles the running speed on its own.
In order for a processor to reach its highest-rated turbo boost clock, a few conditions have to be met:
- Power: Because a higher speed requires more energy, your motherboard must be able to deliver the power necessary for the processor to run at its turbo boost frequency.
- Temperature: The higher amount of power drawn by the processor from the motherboard means that processor also heats more. Thus, the CPU must have a good cooling system that can keep its temperatures in range. Otherwise, if the temperatures go up too much, the processor goes into throttle mode. That means that it automatically lowers its frequency to protect itself from damage caused by overheating.
- Utilization: To reach its rated turbo boost speed, your processor must have a reason to do that. If your apps or games do not need more speed than the base clock, the processor has no reason to increase to its turbo boost clock. Also, if not all the cores of your processor are actively used, there is no reason to activate turbo boost.
Furthermore, modern processors have more than one core, usually going from as few as 2 cores and up to 16 cores. You might be tempted to think that the turbo boost speed advertised for your CPU means that it can reach that maximum frequency on all of its cores, but that might not be the case. Some processors can reach it only on one, two or more of their cores, so understanding what your CPU can offer is even more complicated. However, one thing that you can be sure of is that at least one of the cores on your CPU can reach the turbo boost speed at any given time. The most common situation is that when a multi-core CPU reaches its turbo boost speeds on two of its cores, but the other cores use lower clocks.
To make things confusing Turbo Boost is named differently by manufacturers
Both AMD and Intel have technologies that control their processors' base and turbo boost speeds. For their latest series of computer processors (Ryzen 2000 and Ryzen 3000) AMD calls it Precision Boost 2. You can see a few details about it, in the screenshot below.
Starting with Intel Core i5 and i7 from the second generation, Intel uses Intel Turbo Boost Technology v.2.0, and for the latest Core i7 and i9 processors, it uses Intel Turbo Boost Max Technology v3.0.
Why does the turbo boost clock matter (benefits)?
The main benefit of having a processor which can turbo boost is that it makes your computer faster under heavy load. If you run a video game or a demanding application, your processor automatically increases its boost clock and gives you the best performance it can. That means better performance when it matters most.
Furthermore, turbo boost is a completely automatic process: your processor overclocks itself, without needing any intervention from you. It just works, so everyone gets to benefit, whether a home user with no computer experience or a professional who works with enterprise apps that require heavy processing power.
How to see if your processor is in turbo boost mode
How do you see if your processor runs in turbo boost mode? You can use a specialized app that can monitor your CPU, like CPU-Z, or you can use the Task Manager from Windows.
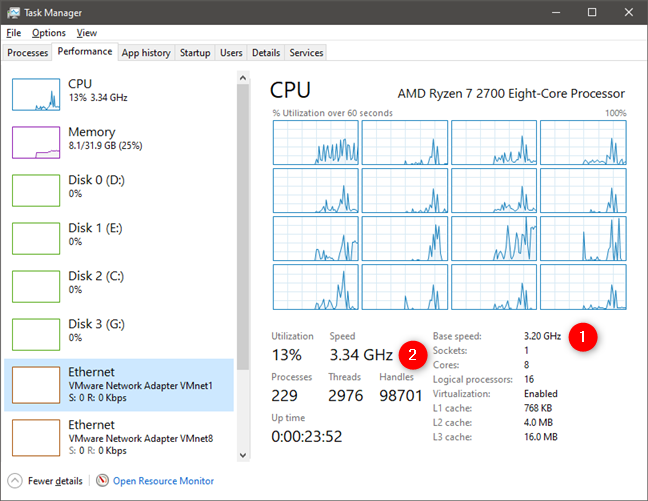
If you prefer not to use third-party apps, launch Task Manager. You can quickly open it by pressing the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys on your keyboard. Then go to the Performance tab and select CPU on the left side of the window. On the right side, under the utilization graph, you see some details and real-time information about your processor. Among them, the Base speed tells you what the base clock of your processor is, and Speed shows you its current speed. If the Speed (2) value is higher than the Base speed (1), it means that your processor is running in turbo boost mode. Here is what we see when an AMD Ryzen 7 2700 processor runs in turbo boost mode:
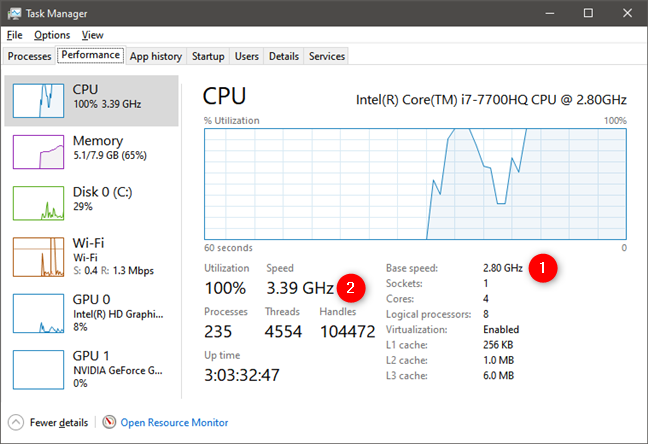
And here's an example of an Intel Core i7-7700HQ processor from one of our laptops:
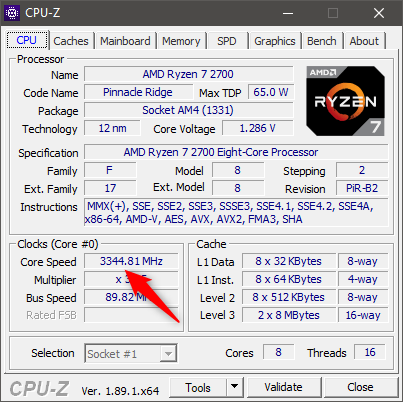
Similarly, third-party apps such as CPU-Z can show you the current speed of your processor in real time. If you are running a demanding app or game, and the current processor frequency is higher than its base clock, as advertised by its manufacturer, then it means that your CPU is running in turbo boost.
What is the Turbo Boost or Precision Boost speed of your processor?
We are curious to know what processor you use, and whether you consider the turbo boost speed to be an important aspect for general system performance. Tell us what you think about AMD's Precision Boost and Intel's Turbo Boost technologies, in a comment below.