Have you ever wondered about Windows environment variables? Maybe some IT admin or computer geek was mentioning them. Did some programs start malfunctioning and returning errors referring to environment variables? Or did you just have an exam, and the only item you didn’t know how to answer was what an environment variable is in Windows? No matter your reasons for wanting to learn more about them, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, I’ll show you what you need to know about environment variables, how they work, and why they are essential for Windows’ well-being:
What are environment variables in Windows?
So, what is an environment variable in Windows? Environment variables are, in short, variables that describe the environment in which apps and programs run. All kinds of programs use environment variables to answer questions like: What’s the name of the computer where I’m installed? What is the name of the user account that is running me? What is my current working directory? Where is Windows installed? Where are the temporary files stored on this computer? Where is the OneDrive folder for this user account?
In Windows, environment variables have a name and a value. For example, the variable windir (short for “Windows directory”) may have the value “C:\Windows” or another path where you installed Windows.
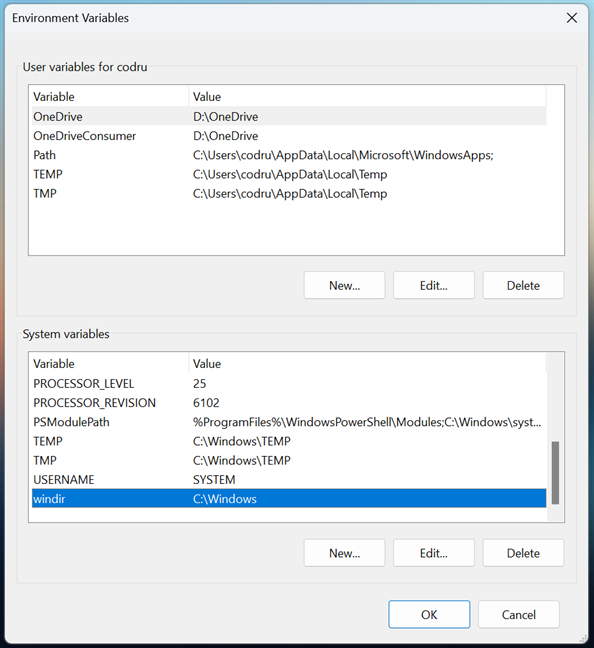
Environment user and system variables in Windows
Another standard variable is named PATH. Many programs need to know where to find specific files, and the PATH variable tells them where to find what they need. Those programs automatically look for a PATH variable, so you don’t have to type it all in every time you run that application. This variable has a value consisting of many user directories. These directories are set by the different applications installed on the computer, and they vary widely from system to system.
The concept of environment variables exists in most operating systems, from Linux to macOS to Windows. In principle, they mean the same thing, but the way they’re implemented and used differs.
What types of Windows environment variables are there?
There are two types of variables: user variables, specific to each user account, and system variables that apply to all user accounts.
User environment variables have values that differ from user to user. As their name implies, they are specific to your user account. They store user-specific data, like the location of your user profile, the folder where temporary files are stored for your account, or the location of your OneDrive folder. That user account can edit them, but other user accounts cannot. These variables can be created and edited by the user, Windows, or different programs working with user-specific locations.
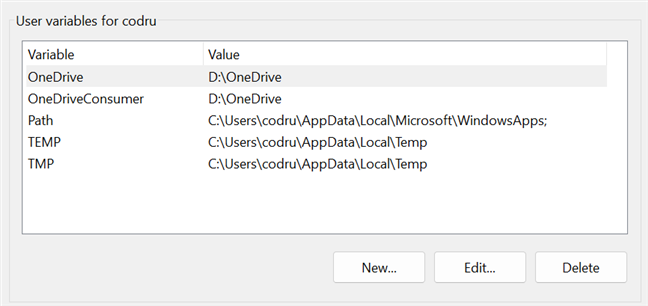
Windows environment User variables
System variables are global and cannot be changed by any user. Their values are the same for all user accounts. They refer to critical system resource locations, like the folder where Windows is installed or the location of Program Files. These variables are set by Windows, different programs, and drivers.
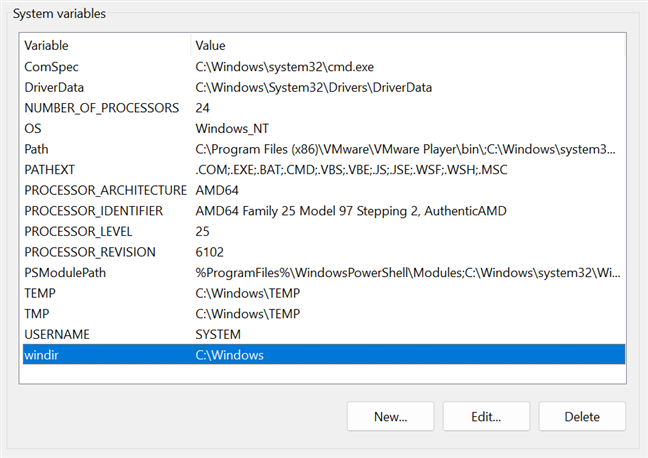
Windows environment System variables
How to find the environment variables in Windows
There are a few different ways to see the list of Windows environment variables. Though pretty similar, there are some slight variations between Windows 11 and Windows 10, so depending on your operating system, read the subchapter below that applies to you:
How to see the list of environment variables in Windows 11
If you’re using Windows 11, a fast way to access environment variables is to use search. In the search box on the taskbar, type environment. After the results show up, click or tap on “Edit the system environment variables.”
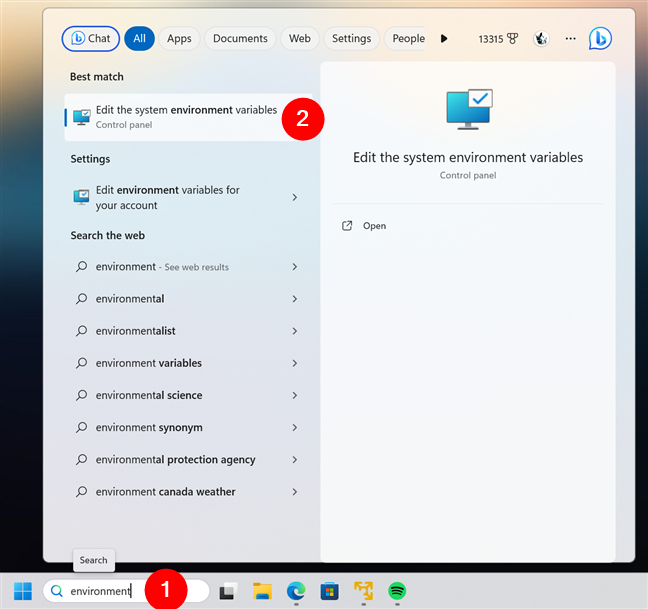
Using search to open the environment variables in Windows 11
As an alternative, you can also get to Windows 11’s environment variables using the Settings app. Open it (Windows + I), select System in the app’s sidebar, and click or tap About in the right-hand pane. Then, click or tap on “Advanced system settings” next to Related links. This opens the System Properties window, where you can access the environment variable by pressing the button with the same name - Environment Variables - from the Advanced tab.
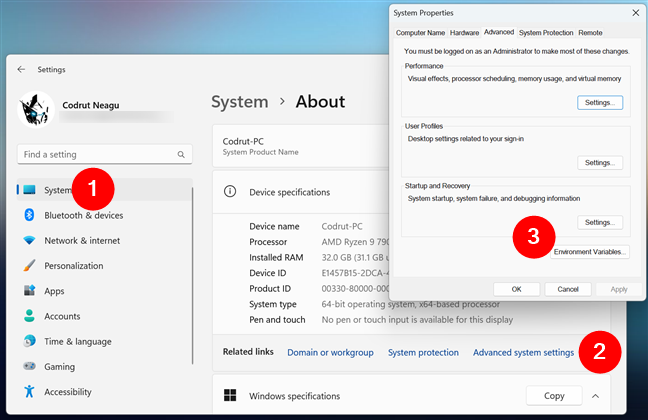
Using Settings to find the environment variables in Windows 11
The third easy method to check Windows 11’s environment variables is to run the next command in the Run window (Win + R):
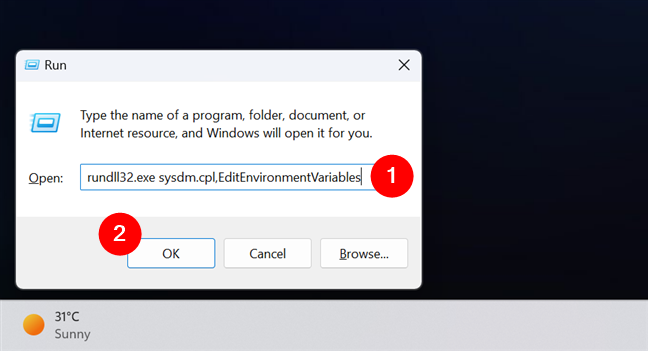
How to show Windows 11's environment variables using Run
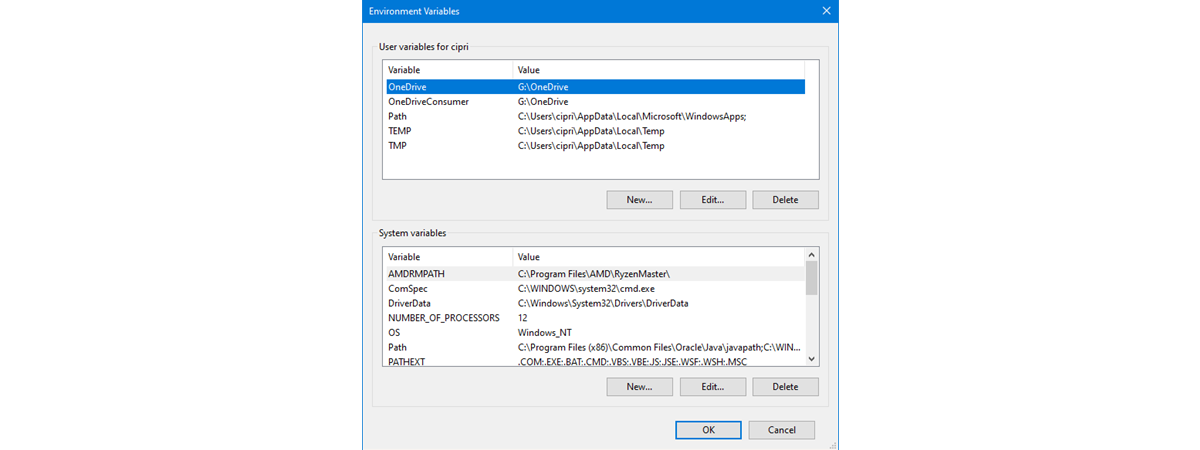
Regardless of the method you decide to use, Windows 11 should open the Environment Variables window. It’s split into two sections: the one at the top lists the user variables that apply to your user account only, while the bottom one lists the system environment variables that are set and used by all user accounts on your Windows 11 computer.
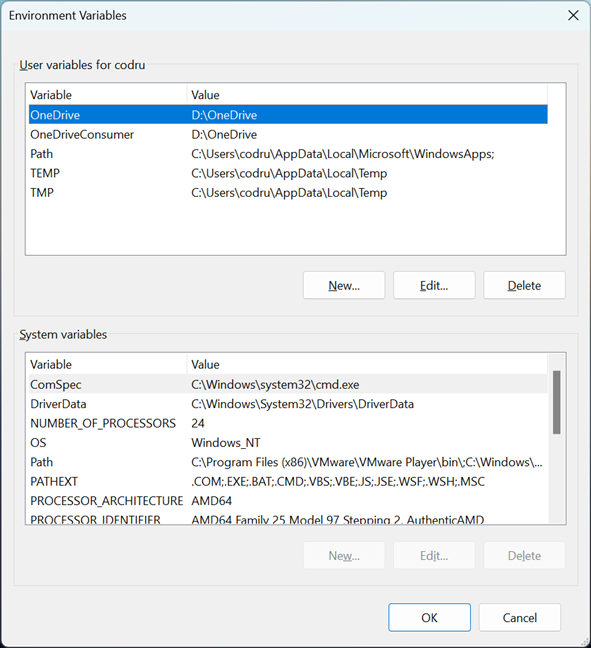
Environment Variables window in Windows 11
TIP: Did you know that you can also make new environment variables in both Windows 11 and Windows 10? Read this guide for details: How to create user variables and system environment variables in Windows.
How to see the list of environment variables in Windows 10
In Windows 10, use the search box on the taskbar to look for environment. Then, click or tap on the “Edit the system environment variables” search result.
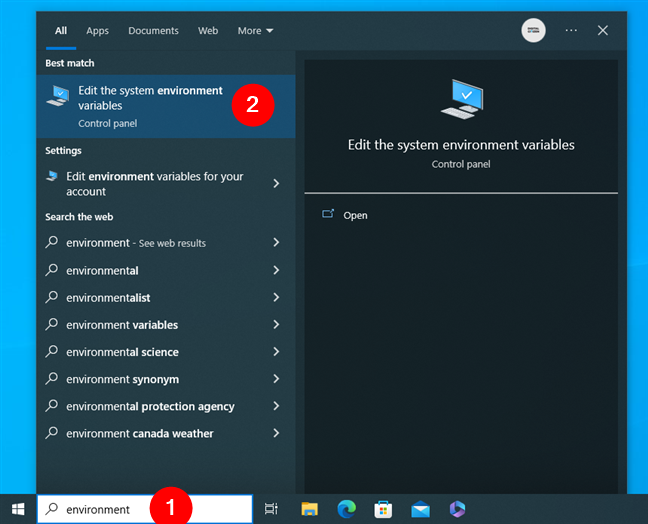
Using search to open the environment variables in Windows 10
Alternatively, you can use the Settings app to access the environment user and system variables. In the Settings app, go to System and select About in the left sidebar. Then, click or tap the “Advanced system settings” link on the right-hand pane. It opens the System Properties window, where you can press the Environment Variables button from the Advanced tab.
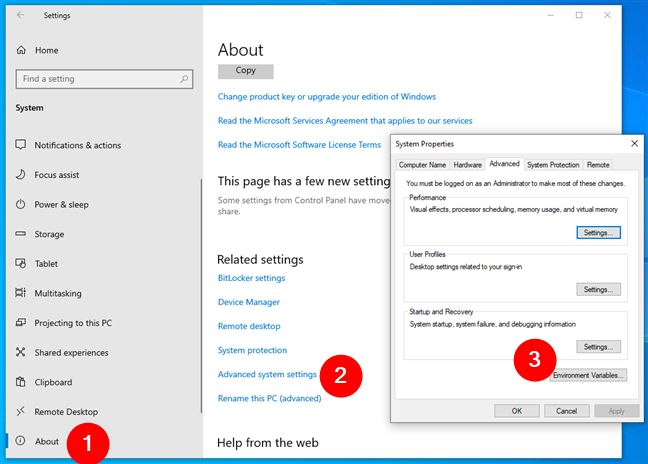
Using Settings to find the environment variables in Windows 10
A third way to see Windows 10’s environment variables is available via the Run window (Win + R). In this window, execute this command:
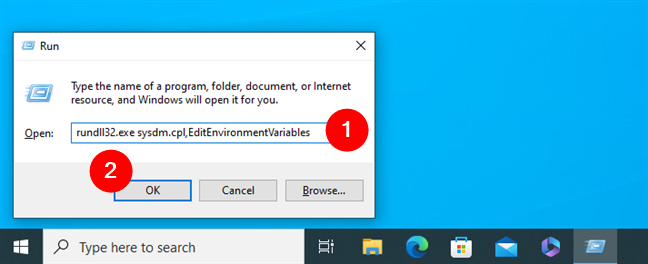
How to show Windows 10's environment variables using Run
Regardless of which method you choose to use, the Environment Variables window should be open now. At the top, the Environment Variables displays your user variables, and on the bottom, it shows the system variables, valid for all the existing user accounts in Windows.
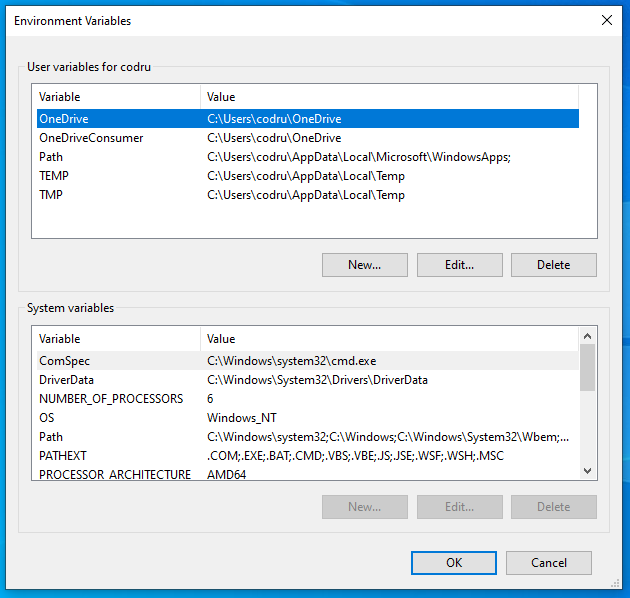
Environment Variables window in Windows 10
TIP: Both Windows 11 and Windows 10 also let you edit environment variables. If you’re curious to know how to do that, you should read this tutorial: How to edit, clear, and delete environment variables in Windows.
How to view environment variables in the command line
Both Windows 11 and Windows 10 also let you see the environment variable from the command line. If this is your preferred way, start Windows Terminal and open a PowerShell or Command Prompt tab in it, depending on which one you favor. Or just open a separate instance of PowerShell or Command Prompt if that’s what you want. Either way, once you do, run one of the commands in the next chapters of this guide, depending on the app you’ve opened.
How to see Windows environment variables in Command Prompt
If you are a fan of the Command Prompt, you can see the environment variables with this simple command:
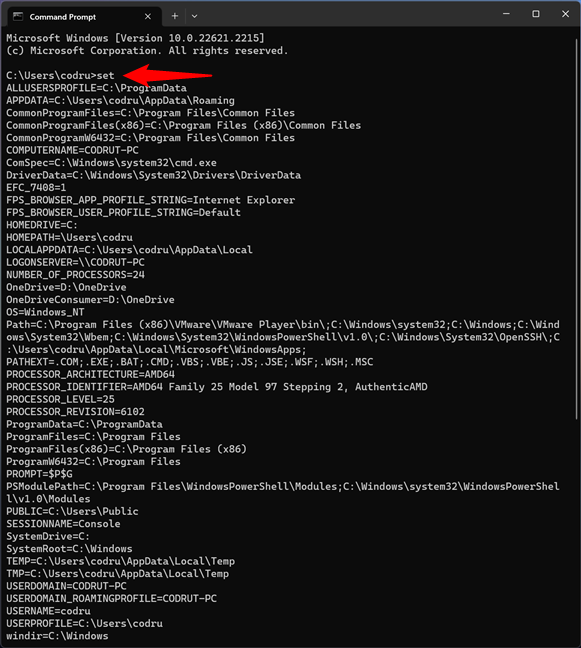
How to see the user's Windows environment variables in CMD
The output of the command lists all the environment variables, including system and user variables.
How to see Windows environment variables in PowerShell
If you prefer PowerShell, the command you have to execute in order to get the list of Windows environment variables is this:
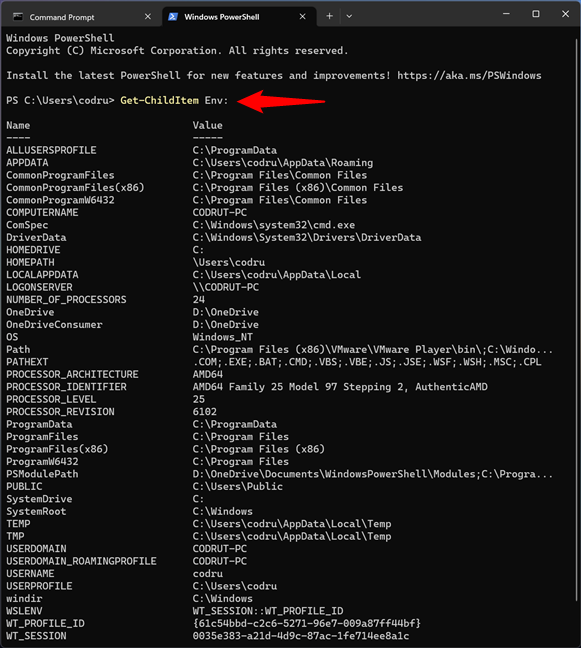
How to see all the Windows environment variables in PowerShell
As you can see, the command lists all the environment variables one after the other, just like in Command Prompt. However, PowerShell also allows you to split the output depending on the type of environment variables you’re interested in (user or system variables):
If you want to see only the system variables, use this command instead:
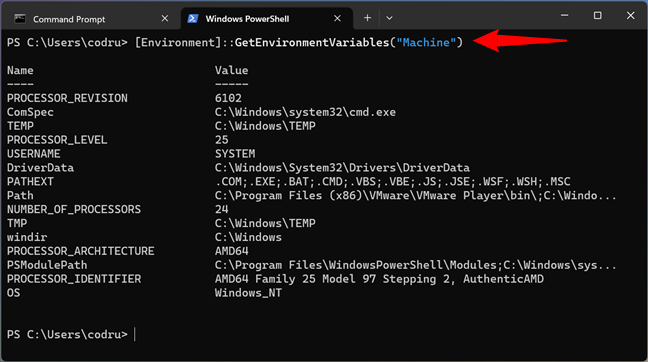
How to see the system Windows environment variables in PowerShell
If you want to list only the user variables, run this command:
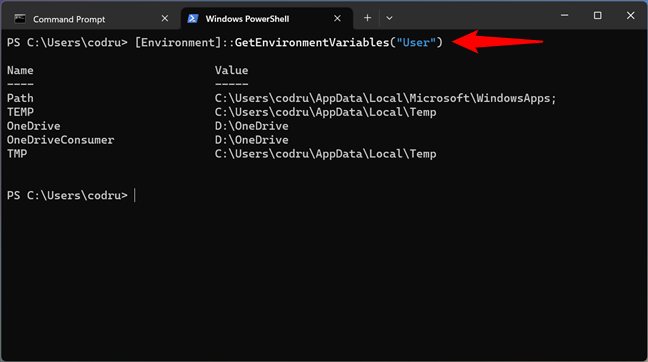
How to see the user's Windows environment variables in PowerShell
These are neater results compared to the ones you get in Command Prompt, isn’t it?
What are the standard environment variables in Windows?
A long list of variables exists on each Windows computer. The most used are variables like OS, PATH, and TEMP. You can find the entire list and all their default values on Wikipedia: Environment variables - Default Values on Microsoft Windows.
Why did you want to know about Windows environment variables?
Now you know how to answer the question: “What are environment variables?”. As you’ve seen, environment variables are neither easy to find nor visible in any way while working with Windows programs. They are managed in the background by the operating system and the different programs and drivers you install. However, they are essential to the proper functioning of your operating system and installed apps. If you change the value of essential system variables without knowing what you are doing, you will experience just how vital these environment variables are by causing your system to malfunction. Before you go, comment below and let me know how you intend to use this information about Windows environment variables.


 04.09.2023
04.09.2023