The Hosts file, a.k.a etc/hosts has been around since 1984. Every operating system has one, including Windows. You may have encountered the term etc/hosts without knowing what it means, and why it is used. If you are a web developer, you surely know what this file is, and you want to find it quickly. In this guide, we explain what the Hosts file is, where it is located in Windows, what a host entry is, and how to edit the Hosts file without stumbling into permission errors. Let's get started:
What is the Hosts file in Windows?
The Hosts file (also referred to as etc/hosts) is a text file used by Windows (and other operating systems) to map IP addresses to host names or domain names. This file acts as a local DNS service, for your local computer, and it overrides the mappings from the DNS server that your computer is connected to, through the network.
Where is the Hosts file located in Windows?
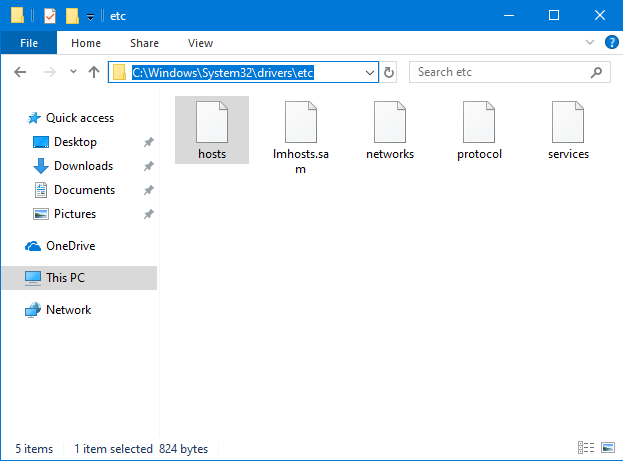
The Hosts files (or etc/hosts) is found in the following folder: "C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc"
It is a file with no file extension, that can be opened and viewed in any text editor, including Notepad.
What is host entry in Windows?
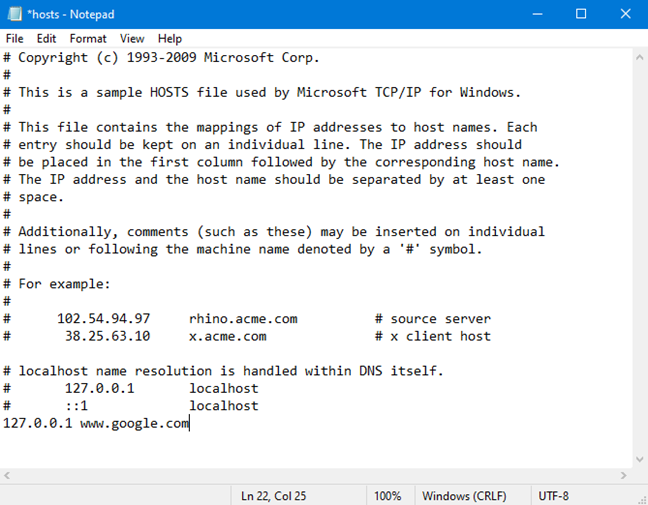
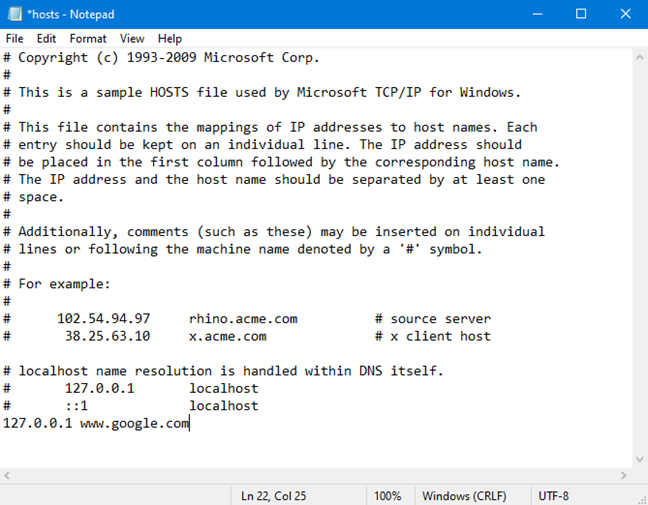
The Hosts file stores host entries. They are standardized lines of text that use the following format: IPaddress Hostname Comment. The first part is the IP address to redirect to, the second part is the domain that you want to redirect, and the third is a comment. The comment is not mandatory only the first two parts are. You can separate the three components of a host entry with spaces or TABs (press the TAB key once or twice). For example, you can add a line that says: "127.0.0.1 www.google.com"
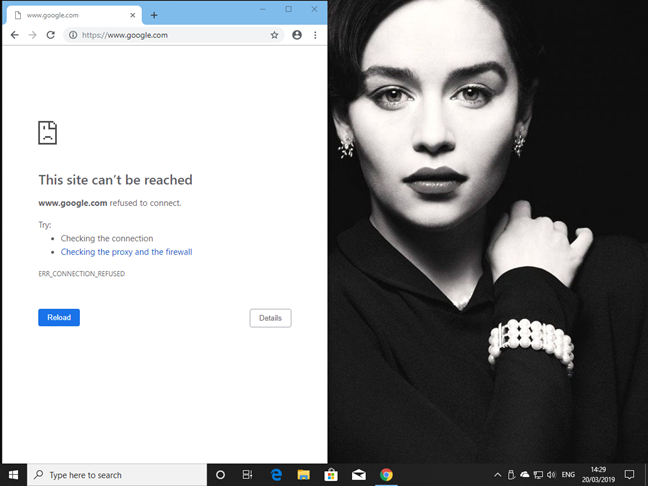
Once you save the entry above, Windows redirects the domain www.google.com to your local computer, in all your apps and web browsers.
What is 127.0.0.1?
127.0.0.1 is a special purpose IP address that leads to the localhost, which is your computer. It is also called "loopback address," meaning an address that leads back to the computer using the address. Unlike standard IP addresses, the loopback address is not associated with any hardware, and it is not physically connected to a network. This address is used by apps and services that are installed on your computer, to communicate with the localhost, meaning your computer.
Your computer also has a unique IP address, different from 127.0.0.1, associated with your network card, that is used to communicate with other devices and services over the network or the internet.
Most often, the localhost IP address is used when installing a web server on your computer, for web development, so that the web pages that are created can be run locally, and tested in a web browser, as if they were live on the internet.
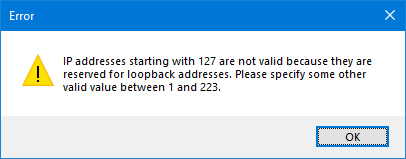
To avoid conflicts in computer networks, the IP addresses used for network devices can be anything except 127.0.0.1. For example, if you manually try to modify the IP address of your network card, in Windows, you receive an error stating that: "IP addresses starting with 127 are not valid because they are reserved for loopback address. Please specify some other valid value between 1 and 223."
How to open and view the Hosts (etc/hosts) file in Windows
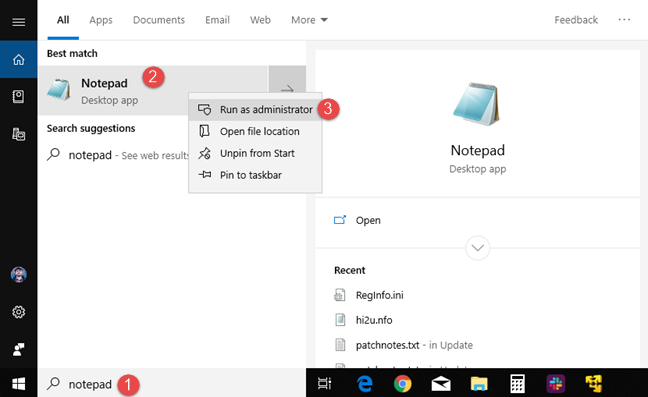
You can edit the Hosts file using any text editor. Let's use Notepad, for example. First, and most important, is that you open Notepad (or your favorite text editor) with administrator permissions. One way to do that is to search for the word "notepad" in Windows 10, right-click (or tap and hold) the Notepad search result, and then click or tap "Run as administrator." In the UAC prompt that is shown, press Yes.
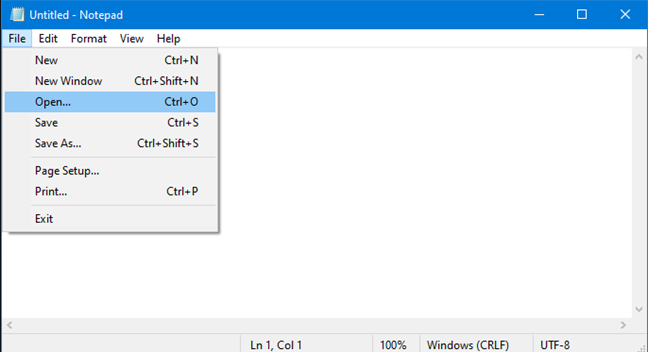
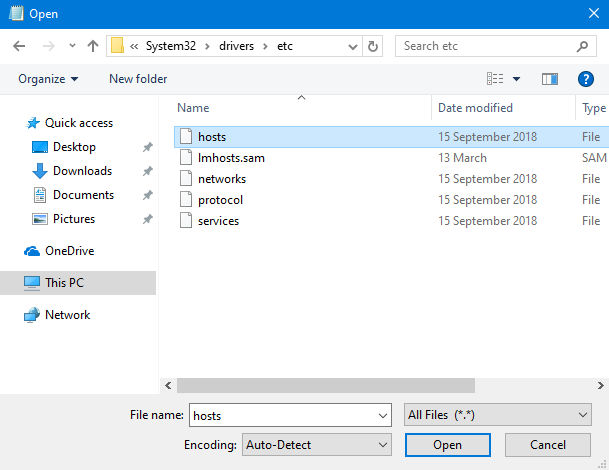
Now you need to open the Hosts file. Click or tap File and then Open, or press CTRL+O on your keyboard.
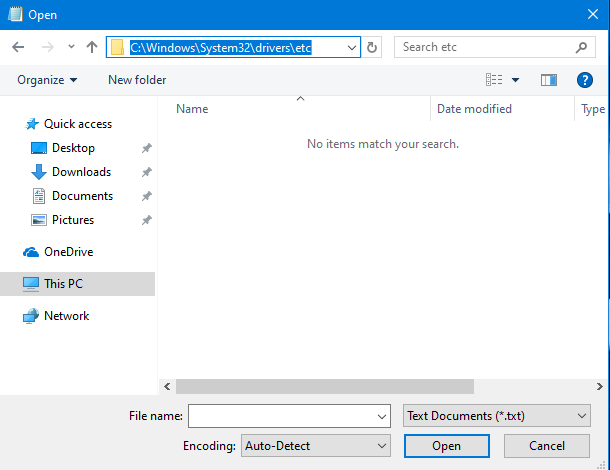
Browse to "C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc" or copy and paste the path in the address field of the Open window, and press Enter.
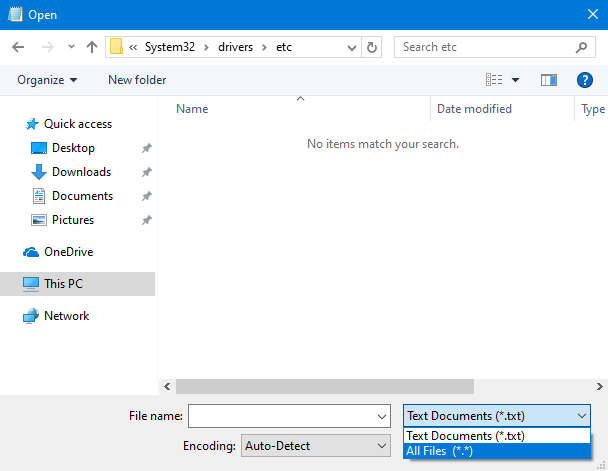
At first, "no items match your search" meaning that you do not see any files. That's because the Hosts file does not have a file extension, and Notepad is looking only for files with the ".txt" extension. Click or tap the drop-down list to the right of the File name field, and choose "All Files (*.*)."
Now you see all the files in the folder, including hosts. Select the file and press Open.
How to edit the Hosts (etc/hosts) file in Windows
After you have opened the Hosts file, you can edit it, and add, change or remove entries, as you do in any other text file.
Remember that all the entries that you add must use this format: IP address Hostname. Add a line like "127.0.0.1 www.google.com" or "192.168.1.1 www.webapp.com"
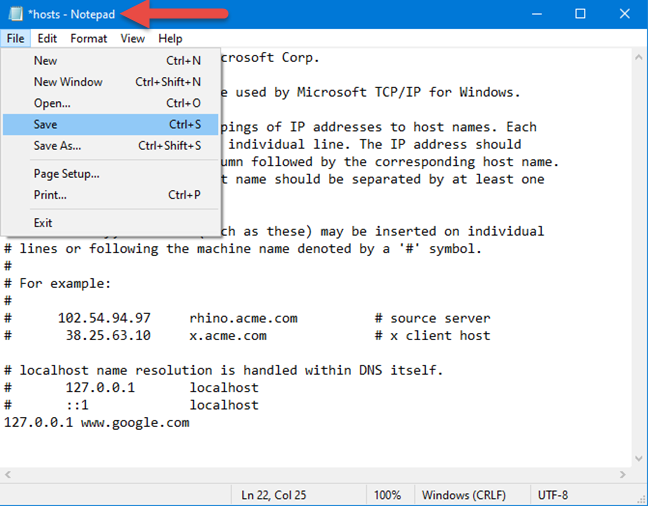
When you are done editing the Hosts file, you need to save your changes. If changes are made and not saved, notice that the tile of the Notepad window starts with a * sign. To save your changes, go to File and then Save or press CTRL+S on your keyboard.
After you have saved your changes, they are applied immediately and override the mappings from the DNS server that your computer is connected to.
Why do people use the Hosts file?
Most casual computer users are not going to use the Hosts file unless they want to pull a prank on someone and use it to block their access to Google, Facebook or some other site, and make them think that it is down, and no longer working. The people using the Hosts file most frequently are web developers who create websites and web apps, which must be tested locally, before publishing them on the internet.
IT professionals also use the Hosts file to block access to specific sites and web resources, on the computers they are managing at work. For example, they can use it to block advertising in their business network, from specific ad networks.
Malware can also use the Hosts file to redirect your web traffic to remotely controlled servers and steal personal information or other data.
I can't edit the Hosts file in Windows! What do I do?
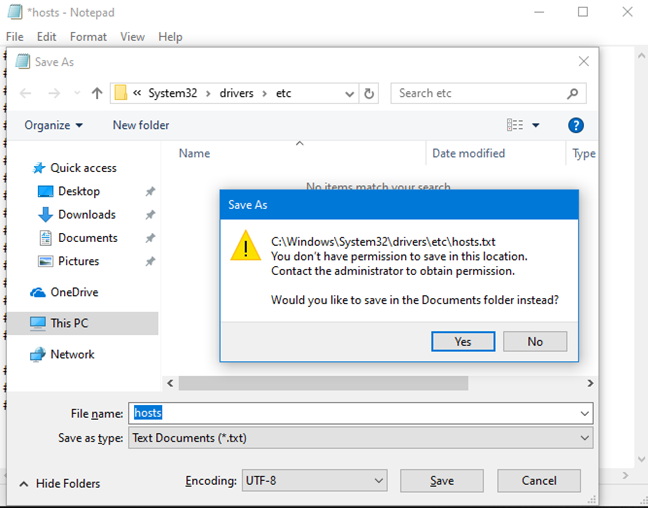
When editing and saving the Hosts file in Windows, you may receive an error message that states: "You don't have permissions to save to this location." This happens because you did not open Notepad or the text editor that you are using, with administrator permissions. Read the sections above and see how to start Notepad with administrator permissions.
After you do that, you can edit the Hosts file without any errors and permission problems.
How do you use the Hosts file in Windows?
Thank you for reading this tutorial. We hope that we have managed to answer all your questions about the Hosts file. Before closing, tell us in a comment, how you plan to use the Hosts file in Windows? Is it for work or just prank on a friend or family member? Comment below and let's share our experiences working with the Hosts file.


 21.03.2019
21.03.2019