If you’re shopping for a new desktop processor in late 2024, you’re probably wondering what to choose: AMD or Intel? Is Ryzen better than Intel, or does Intel still make better processors? In the Intel vs. AMD competition, the winner is seldom easy to tell, especially for gaming. Both brands offer a large range of processors, some high-end and powerful, others more budget-friendly. So what are the pros and cons of AMD vs. Intel? To help you out, I decided to update my AMD vs. Intel comparison. Read on and see what aspects you should take into consideration when comparing the latest Ryzen and Intel Core processors in 2024:
AMD vs. Intel processors: Manufacturing process, heat, and power consumption
Both AMD and Intel have capable processors; there’s no question about it. However, when it comes to specs, there are some differences between them. While Intel was almost always first in technological advances in the past, AMD has been overshadowing it in the last couple of years, and both companies seem equally advanced today.
One key factor determining a processor’s performance and efficiency is the manufacturing process, also known as lithography or the node. This refers to the size of the processor’s transistors, measured in nanometers (nm). The smaller the transistors, the more they can fit on a chip, resulting in higher performance and lower power consumption.
AMD has been ahead of Intel in this aspect for several years, thanks to its partnership with TSMC, a leading semiconductor foundry. AMD’s latest Zen 4 CPUs (Ryzen 7000 and Ryzen 8000 series) use 5 and 4-nanometer manufacturing processes. This allows them to pack more cores and cache, as well as features like 3D stacking technology (X3D) that boost performance even further.
AMD’s Ryzen 9000 Series continues this collaboration (with TSMC), using 4-nanometer lithography in its Zen 5 architecture. This manufacturing process allows AMD to pack more transistors on the chip, improving both performance and efficiency. AMD’s Ryzen 9000 series builds on the energy efficiency that the Ryzen 7000 series is already known for, making it a leader in power consumption and thermals, particularly in multi-core workloads.
On the other hand, Intel has been struggling with its manufacturing process, which has caused delays and setbacks for its products. Therefore, Intel still uses a 10-nanometer process for its 13th and 14th Gen Core processors. However, the company tweaked its CPUs, which use a hybrid architecture with two types of cores: high-performance and power-efficient, similar to smartphone processors. Thanks to this approach, many of Intel’s latest processors can match or, in certain cases, even outmatch AMD’s models.

AMD vs Intel
All that leads to a series of benefits and disadvantages for both AMD’s Ryzen processors and their Intel counterparts:
- Thanks to the smaller manufacturing process, Ryzen CPUs have an increased density of transistors per mm². Therefore, AMD processors are typically more power-efficient and cooler (lower TDP) than similar Intel processors.
- Despite improvements in their hybrid design, Intel processors still tend to consume more power and generate more heat than AMD processors.
The latest Intel Core processors can use their high-performance cores for demanding tasks (like games) and their efficient cores for less demanding ones. This means that Intel processors’ performance, heat, and TDP can vary greatly depending on what you’re doing. For instance, they can stay cool and power-efficient during office work, but when they need to increase performance, like in games or video editing software, the cost is a significantly higher amount of electricity consumed. Plus, more heat is created. AMD processors are generally more energy-efficient than Intel processors, requiring less power for the same or higher level of performance. They also tend to consume lesser amounts of electricity when performing light tasks.
Overall, it’s evident that AMD and Intel have different approaches when making their processors. Each one has its own strengths and weaknesses, but I think it’s quite clear that AMD is better than Intel when it comes to the manufacturing process, heat, and power consumption, offering high-performance and energy-efficient processors. Still, with its hybrid CPU design, Intel manages to balance performance and power efficiency, although not as well as AMD.
AMD vs. Intel processors: Performance
Intel has a tradition of delivering desktop processors with incredible single-core speeds, and that’s still true for the 13th Gen and especially the 14th Gen Core lineup. Many of these Intel processors can run at speeds higher than 5.0 GHz, and some reach the 6.0 GHz threshold! The fastest of the bunch are the Intel Core i9-14900K, i9-14900KF, and i9-13900KS, all of which can boost to 6.0 GHz!
However, AMD’s processors are not far behind either, reaching almost similar single-core speeds and performance. All Ryzen 9000 processors and most of the Ryzen 7000 and Ryzen 8000 launched thus far feature maximum turbo speeds of over 5.0 GHz! The most powerful are the AMD Ryzen 9 9950X, AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D, and the AMD Ryzen 9 7950X, and all of them can run at a maximum speed of 5.70 GHz!
The Zen 5 and Zen 4 architectures make the Ryzen 9000, 8000, 7000 series processors capable of delivering higher boost clocks than ever before. Looking back to the past, Ryzen 5000 CPUs promised and offered up to 19% more IPC (instructions per cycle/clock) than previous Zen 2 Ryzen 3000 processors, plus lower cache latency. The Zen 4 architecture used for Ryzen 7000 and 8000 CPUs brings an approximate 13% IPC uplift over predecessors and up to 29% higher single-thread performance! Furthermore, the Zen 5 architecture used to create the Ryzen 9000 series brings another 16% IPC uplift (on average) over its predecessors.

Is AMD Ryzen better than Intel?
Intel’s hybrid architecture delivers incredible performance. The Raptor Lake processors can deliver up to 15% more single-thread performance and up to 41% more multi-thread performance than the previous CPUs. On a trip down memory lane, it’s interesting to remember that the old Alder Lake lineup featured a similar 19% increase in instructions per cycle/clock compared to previous Intel processors. The 14th Gen Intel Core (Raptor Lake Refresh) series is a minor update to Raptor Lake, using the same hybrid architecture but with slightly higher clock speeds and a bit lower power consumption.
Here’s a table I compiled with AMD’s current processor lineup (Autumn 2024), their technical specifications, and retail prices:
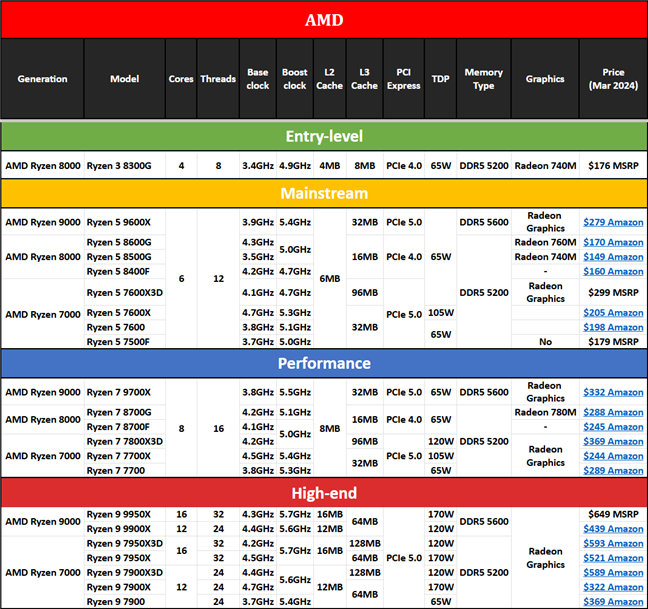
AMD Ryzen 7000, 8000 & 9000 series CPUs specs, features, and prices
Regarding cache memory, the 5 and 4-nm lithographies allow AMD to bundle more of it on its Ryzen processors than Intel can. Throughout the AMD Ryzen 7000, 8000, and 9000 lineups, we get between 8 to 64 MB of Level 3 cache memory. Even more on the “3D special” processors designed for gaming performance, where AMD uses 3D V-Cache in amounts of 96 or 128 MB! Intel is behind in this regard, with its Raptor Lake and Raptor Lake Refresh CPUs getting only 12 to 36 MB of Smart Cache memory.
AMD vs. Intel processors: Features
All the AMD Ryzen 9000 (Zen 5) and 7000 (Zen 4) desktop processors fully support PCI Express 5.0! As all their lanes are PCIe 5, they have a lot of bandwidth available for both the discrete graphics card and all the other components using this interface, such as M.2 NVMe solid-state drives!
Intel’s Gen 13 and Gen 14 Core processors also support PCI Express 5.0, but only for the x16 graphics port. These CPUs give you the best performance possible from present and future high-end graphics cards that are PCIe 5-compatible. However, the other PCIe lanes are limited to version 4.0, including those that go to the M.2 slots where you connect your SSDs.

Is Intel better than AMD?
AMD’s Ryzen 8000 series lags behind with support only for PCI Express 4. However, most of the Ryzen 8000 processors are APUs (accelerated processing units) that include both traditional CPU cores and advanced integrated graphics. Except for the Ryzen 5 8400F and the Ryzen 7 8700F, which don’t have integrated graphics, the other Ryzen 8000 processors are designed to work without a discrete GPU and have enough power to run AAA games in 1080p resolutions on their own. The Ryzen 8000 processors don’t really need PCIe 5 for that. However, it would’ve been nice to be able to use fast PCIe 5.0 solid-state drives with them.
Regarding memory support, on the one hand, all Intel’s 13th Gen and 14th Gen Core processors support DDR4 RAM running at 3200 MHz. All of them can use DDR5-4800 as well, and higher-end models also offer support for DDR5-5600. Pay attention, however: you’ll have to choose the right motherboard right from the start, as you can only use one type of RAM on any given motherboard. There are some designed for DDR4, and then there are others meant for DDR5.
On the other hand, AMD’s Ryzen 9000, 7000, and Ryzen 8000 processors only work with DDR5, meaning you’ll need a motherboard and DDR5 memory to accompany any such processor.
Take a look at the table below to see what Intel’s 13 and 14 Gen Core processors offer and what their real prices are today:

Gen 13 & 14 Intel Core processors specs, features, and prices
Last but not least, when it comes to integrated graphics, both Intel Core and AMD Ryzen processors have built-in GPUs. With Intel, it depends on the exact CPU model you’re looking at. It’s easier with AMD: almost all Ryzen 9000, 8000, and 7000 processors have integrated graphics chips, except for the AMD Ryzen 5 7500F, the Ryzen 5 8400F, and the Ryzen 7 8700F.
The integrated graphics options available on AMD Ryzen 9000, Ryzen 7000 and some of Intel’s 13 and 14th-gen Core desktop processors are pretty basic. They can be handy in some computer configurations built for office work but not much else.
The graphics chips built into the AMD Ryzen 8000 processors are another matter, though. As I briefly mentioned earlier, the integrated graphics on these AMD CPUs are quite powerful - significantly more powerful than what you get on other AMD Ryzen or Intel Core models. The AMD Ryzen 8000 processors can run most AAA games at 1080p resolution, although they may sometimes require lower-quality settings. While they’re not designed to compete with or replace dedicated graphics cards, they are undoubtedly the best option on the market for iGPU gaming.
In conclusion, if you want to future-proof your computer, you’ll be better prepared with an AMD Ryzen 9000, as that gives you DDR5 support and PCIe 5.0 for your GPU and SSDs. A 13th or 14th-generation Intel Core CPU will give you the same benefits, except that your SSD slot(s) will be limited to PCIe 4.0.
If you need to keep your budget in check, you might want to get an AMD Ryzen 8000 CPU or an Intel Core processor from the 12th or 13th generation. The former lets you play games without having to buy a discrete GPU, while the latter allows you to save some money by using DDR4 memory.
AMD Ryzen vs. Intel Core: Price, value, what to choose?
The question on everyone’s lips is probably which processors offer the best price-per-value, and that’s important to know. For regular daily work, both AMD and Intel processors are excellent choices, and entry-level and mainstream AMD Ryzen processors come at similar prices. However, things are not as clear regarding performance and high-end models. Furthermore, it gets even blurrier when looking at the two generations of processors each company manufactures today.
Most of Intel’s 13-generation Core processors and AMD’s Ryzen 7000s are on sale these days. With Intel, prices seem to have been slashed by up to 35%! AMD’s processors, however, seem to have even bigger price cuts, some of them going over 40% down their initial rates!
If you want to build a computer for office work, you might not need or want the best performance. It’s possible to find cheap bundles with entry-level Intel Core processors. They can run on DDR4, which is more affordable than DDR5. When building office computers, the prices you can find now should be a strong factor in your choice between Intel and AMD.
If you’re looking for gaming on a budget, you should probably go with an AMD Ryzen 8000. These CPUs deliver impressive integrated graphics performance for desktop PCs, and you don’t need to buy a separate graphics card.
A mainstream AMD Ryzen 7000 or an Intel Core 13/14th-Gen CPU may also do the job. Such AMD processors are heavily discounted right now, which means you can spend a bit more on the motherboard and DDR5 memory. With similar Intel Core CPUs, you can save by using your old DDR4. Or, if you have to buy DDR4, it’s more affordable anyway.
Last but not least, if you’re looking for top-notch performance in any workload, be that gaming, video editing, CAD applications, etc., then you should check out higher-end AMD Ryzen 9000 or 14th-Gen Intel Core processors and pair them with DDR5 and appropriate motherboards. Whether you go with Intel or AMD, be ready to spend quite a lot of money on either path you choose.
Intel’s Core i9-14900K processor is the best right now, so if you need maximum brute performance, get it without hesitation. However, consider the fact that it can only work with PCIe 4.0 SSDs. If you want to futureproof your PC and be ready for what’s next, you may want to go with an AMD Ryzen 9000 series processor instead. The AMD Ryzen 9 9950X, for instance, offers similar performance to the Intel Core i9-14900K and also has a significantly lower power consumption. In today’s chaotic energy market, this is an important plus.
Check the following comparison chart for AMD vs. Intel processors if you’d like to see how they stack up against each other. I tried to cover all the essential details of both companies’ current desktop processors, including real-world prices from the Amazon Intel Store and Amazon AMD Store (where a CPU is not available on Amazon, I’ve mentioned the manufacturer-suggested retail price - MSRP) to help you make an informed decision:
You can also download the Excel spreadsheet above, using this link.
Intel vs. AMD: Which one’s the best in 2024?
In conclusion, there’s no clear answer to which one’s the best: AMD vs. Intel. Both companies offer great desktop CPUs, but the best choice depends on your specific needs and preferences. AMD Ryzen processors excel in power efficiency and multi-core performance, making them ideal for productivity tasks and building future-proof computers. On the other hand, Intel Core processors still lead in single-core speeds and offer a hybrid architecture, which is particularly appealing for gamers and those looking for peak performance in single-threaded tasks. Before deciding, you need to find what matters most to you: Do you need more cores for multitasking or faster clock speeds for gaming? Are power efficiency and features like PCIe 5.0 and DDR5 support more important? Taking all that into account, which do you think is better for you: AMD or Intel? Let me know in the comments section below.


 11.10.2024
11.10.2024