Do you have a new DSLR camera, an action camera, or maybe a new smartphone? Do you want to add a memory card to it? Are you wondering how to choose the right memory card? Before you do that, you need to understand what are the different types of memory cards out there, and which fits your specific device. Read this article to see the most common memory cards used right now, what their names mean, what Speed Class ratings are, and more:
What is a memory card?
Memory cards are small electronic devices designed to store information. They typically use flash memory, just like USB memory sticks or solid-state drives. Memory cards are used inside digital cameras, smartphones, tablets, media players, laptops, mobile consoles, surveillance cameras, and even in some desktop computers. Because they use flash memory, the information saved on a memory card is not lost when you unplug it. It also means that you can copy, move, and delete files, as well as format memory cards whenever you want.
Unlike USB flash drives, for memory cards, you don't use a USB port to plug them into other devices. Instead, memory cards directly connect via special hardware interfaces, called slots, available on the devices that support them.
How many different types of memory cards are there?
Decades ago, there were many different types of memory cards available, created by many hardware manufacturers. Although many companies tried to set their own memory card standards, only a few have managed to win the competition. Today, most memory cards are part of one of the two main families: Secure Digital and CompactFlash. Let's see what each of them has to offer:
What are the different types of SD cards?
Secure Digital, better known by its SD acronym, includes many different types of SD cards, with different shapes and sizes:
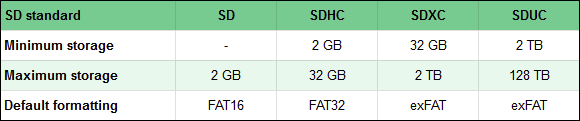
- SD (Secure Digital) - an old type of memory card that has storage capacities up to 2 GB, formatted by default in FAT16. SD cards have a physical size of 32 × 24 × 2.1 mm. This size has become the norm for all the other, newer versions of SD cards, such as SDHC, SDXC, or SDUC. Nowadays, many people are using the term SD to refer to the newer SDHC, SDXC, or SDUC memory cards too.
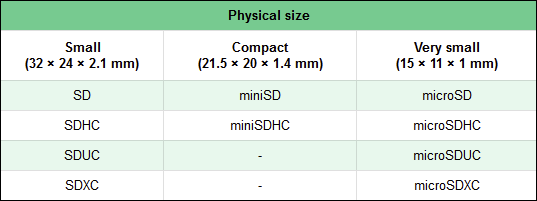
- microSD are miniaturized versions of SD cards, which have a standard size of 15 × 11 × 1 mm. microSD is also an old type of memory card, with a maximum storage capacity of 2 GB. Their physical size was kept for the newer versions of microSDHC, microSDXC, and microSDUC cards. Also, people refer to these cards as microSD cards, although that is not technically correct.
- miniSD cards are smaller than regular SD cards but larger than microSD cards: 21.5 × 20 × 1.4 mm. Otherwise, they have the same storage capacity range as SD/microSD cards.
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) cards are identical to SD in terms of size, dimensions, and speed, but have a range of storage capacity between 2 GB and 32 GB. Also, SDHC cards are formatted by default in FAT32.
- microSDHC is the miniaturized version of SDHC. microSDHC cards can also store up to 32 GB of data on them.
- miniSDHC cards have the same body size as miniSD cards, but the same specs as SDHC, with a storage size of up to 32 GB.
- SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity) is an improved version of SDHC. While keeping the same physical aspects as SD, SDXC cards can hold up to 2 TB of files, and also provide faster data transfer speeds. SDXC cards are formatted, by default, using the exFAT file system.
- microSDXC cards have the same physical size as microSD and microSDHC cards, but they're faster, and their storage capacity can theoretically go up to 2 TB.
- SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity) cards retain the same physical build of SD/SDHC/SDXC cards, but their maximum storage capacity is much greater, with a theoretical maximum of 128 TB. By default, SDUC cards come formatted using exFAT.
- microSDUC is the miniaturized version of SDUC. They have the same size as microSD/microSDHC/microSDXC cards, but all the benefits in speed and storage space of regular SDUC cards.
To help you make sense of all this data, take a look at the comparison below:
As you might have noticed from the list, we did not mention miniSDXC or miniSDUC cards. That's because this size format has been abandoned, and there are no such memory cards available on the market.
How fast are SD memory cards, and what does card speed class mean?
When referring to the speed of SD cards, the ratings and classifications you see on them refer to the sequential read and/or write speeds. The main factor to take into consideration when you're looking at the advertised speeds of an SD card is how fast its bus is. For example, on some SD cards, you might see things such as UHS or UHS-II printed by their manufacturers.
This information can help you understand how fast an SD card is rated to be, under normal conditions. The commonly used buses on SD cards nowadays are:
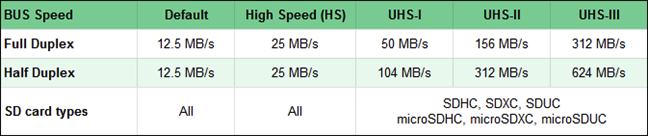
- Default bus speed means that the SD card with this rating (or no rating at all) can read and write data at up to 12.5 MB/s.
- High Speed (HS) offers double the default speed - 25 MB/s for both reading and writing data on the SD card.
- UHS-I (Ultra High Speed I) SD cards can reach a read/write speed of 50 MB/s (full-duplex) when data is transferred both ways and up to 104 MB/s when data is transferred one way only (half-duplex, read or write).
- UHS-II (Ultra High-Speed II) increases the read/write speeds up to 156 MB/s in full-duplex and 312 MB/s in half-duplex.
- UHS-III (Ultra High Speed III) goes even higher, reaching 312 MB/s in full-duplex mode and 624 MB/s in half-duplex mode.
The UHS buses are only found on SDHC, SDXC, SDUC cards, and their micro variants. UHS buses are not supported by first generation SD cards.
The second important factor in determining the read and write speeds of an SD card is its Class rating. This rating tells us the minimum sustained speed of a memory card, measured in transferred megabytes per second. SD Class ratings are divided into three different categories:
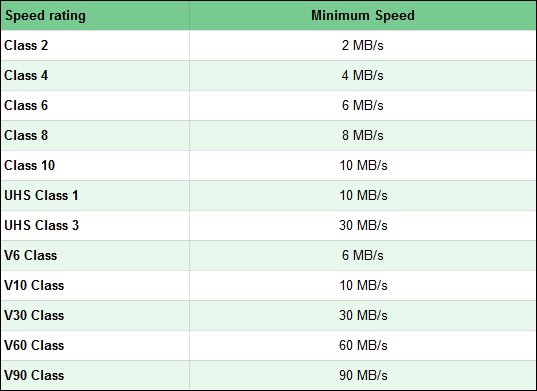
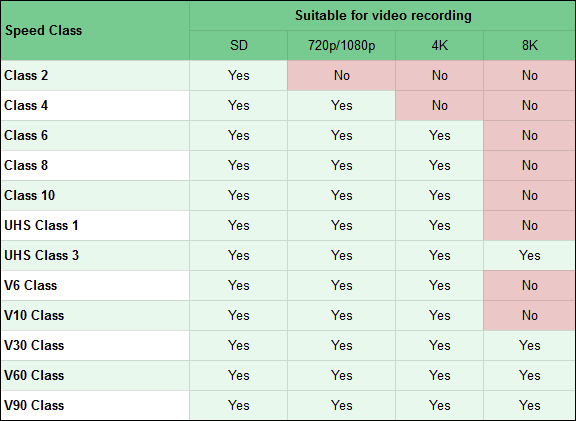
- Speed Class is used for SDHC memory cards and can be equal to 2, 4, 6, 8, or 10. Each number tells you the minimum speed expressed in MB/s. For example, a Speed Class of 2 means that the memory card has a minimum sustained speed of 2 MB/s. A Class 10 SD card has a minimum speed of 10 MB/s, and so on.
- UHS Speed Class is a speed rating used for SDHC and SDXC memory cards that use a UHS bus. The UHS Speed Classes can have one of two values: 1 or 3. A memory card with UHS Class 1 means its minimum speed is equal to 10 MB/s, while a UHS Class 3 card has a minimum speed of 30 MB/s.
- Video Speed Class, or V Class in short, is used as a rating for memory cards designed to work with video recording devices. This rating assures you that a card can support the minimum speeds needed for recording video. There are five V Classes: V6, V10, V30, V60, and V90. The numbers that come after V tell you the minimum sustained speed of the card. For example, V10 means that the card has a transfer speed of at least 10 MB/s in the worst scenario, V60 works at a minimum speed of 60 MB/s, and so on.
To summarize the speed differences, take a look at the table below:
One of the most common use cases for SD cards is for providing storage space for video recordings. Whether you use a video camera, an action cam, or even a smartphone, it is not enough to just buy a memory card with a lot of space for your recordings. You should also take a good look at how fast that memory card is, to make sure that it can handle video recording in the resolution you prefer. Read the table below, where you can see what Speed Classes your card should have for different types of video recording scenarios:
What is Compact Flash and who's using CF memory cards?
CompactFlash, known by many under its acronym CF, is a memory card format that's mainly used in professional and high-end digital photo and video cameras. Canon and Nikon are among the companies that choose to use CompactFlash on their electronic devices.
In the past, CF cards used to offer both larger storage capacities and faster data transfer speeds than other types of memory cards did. That's why CompactFlash cards were preferred by photo and video professionals. Some also liked CF cards more because of their bigger physical size, which made them easier to handle and harder to lose.
Because of their larger storage capacity, as well as their fast speeds, CompactFlash cards have held well on the market and are still used and available today. There are two types of CF cards:
- CompactFlash I cards have storage capacities that can go up to 128 PB (maximum available in the real world right now is 512 GB) and a standard physical size of 43 × 36 × 3.3 mm.
- CompactFlash II cards have the same specs as Type I but are thicker: 43 × 36 × 5 mm.
CompactFlash has been superseded by CFexpress, a type of memory cards that can be incredibly fast, as they're using PCI Express 3.0 and support NVMe. Unfortunately, CFexpress cards are not backward compatible with CF slots, as they have both different physical sizes (38.5 × 29.8 × 3.8 mm) and use newer technologies.
Do you have any other questions about memory cards?
We hope that this article has been helpful and that you now have a better grasp of the different types of memory cards. Before closing, tell us if you have any other questions about memory cards. Do you have anything to add to our guide? Use the comments section below to let us know.


 14.05.2020
14.05.2020