The USB technology has been around for almost three decades now. We’ve become so used to it that we take it for granted and don’t consider it special. Although you surely used a USB device, it is possible that you don’t really know what USB means and what it does. You might have heard some acronyms like USB Type C or USB 3, but maybe you want to know more. In this article, I’ll explain what USB is, give you a bit of history about this standard, and share the differences between the different types of USB ports and versions. If you’d like to have a better understanding of terms such as USB Type C, USB 3.0, or USB 3.2, read on:
What does USB stand for?
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, and it represents an industry standard for cables, connectors, and communications protocols used for the connection, communication, and power supply between various computing devices. It is used by many devices, ranging from the common keyboard and mouse to cameras, printers, scanners, flash drives, external drives, smartphones, tablets, TVs, etc.

USB logos and specifications
The Universal Serial Bus is a plug-and-play interface, meaning that you can connect a device with a USB port to your computer, and the computer will be able to automatically detect and install the device, although sometimes you will have to provide the necessary drivers for your operating system. In order to act as a means of communication, USB can transfer data to and from the devices it connects, like from your computer to your keyboard and the other way around.
USB can also supply power to devices. This feature is one of its most useful traits because not only does it allow you to make your devices communicate between them, but it also lets you power them or charge their batteries. For instance, smartphones have a USB port that’s used both for data transfers and for charging their batteries. Similarly, many new laptops charge their batteries exclusively through a USB port and without using separate power adapters.
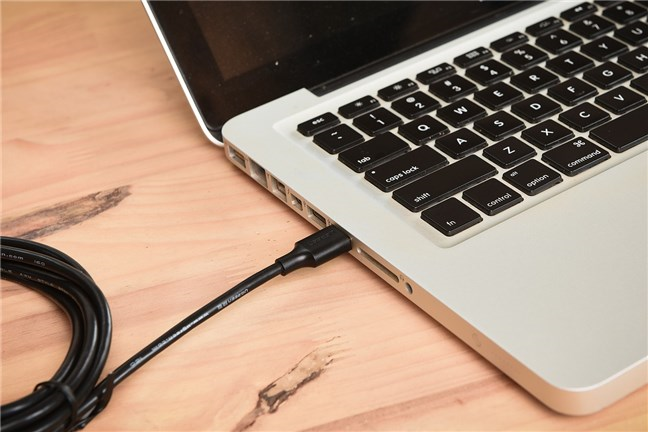

USB port on a laptop (used for charging)
TIP: In case you’re wondering why USB is called a bus, a cool piece of information is that in the old days of computing, the term “bus” was used to refer to a shared line of communication between various hardware components in a computer. That’s why USB is called a bus: because it allows multiple devices to communicate with your PC. 🙂
A very brief history of the USB standard
The Universal Serial Bus, or USB in short, was designed in 1996 by several key companies: Compaq, DEC, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, NEC, and Nortel.

USB Type-A connector
Before USB was invented, computers used to connect to peripherals like keyboards, mice, printers, scanners, and cameras by using various types of ports and connections. For instance, before USB was adopted, keyboards and mice were usually connected via PS/2 connectors or by using serial ports. Printers and scanners did the same via parallel ports. And if you were a gamer back then, you also needed a game port to play games on your computer using a joystick or a gamepad. Just take a look at the examples from the picture below:
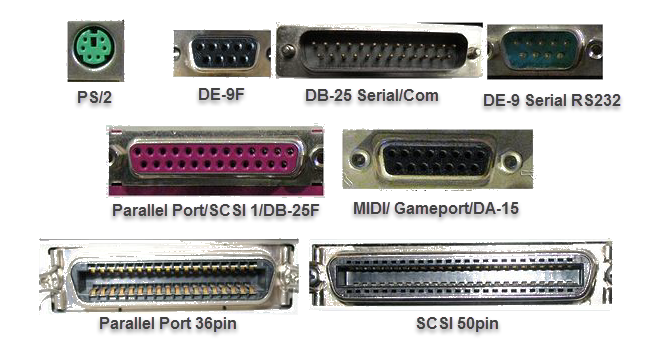
Old types of computer ports
The first USB ports were incapable of high-speed transfers, and hardware manufacturers did not embrace this interface right from the start. But a few years after it was first developed, the USB interface was revised by the companies that created it, and they made USB version 2.0, which was a lot faster. Because of that, after the year 2000, the USB port saw a massive expansion, and it is now found on all kinds of devices. Since then, USB has become the main way of connecting devices and transferring data between them.
USB speeds and versions
Since it was first developed, the USB interface kept getting faster with each revision. Here are the main revisions or versions of USB:
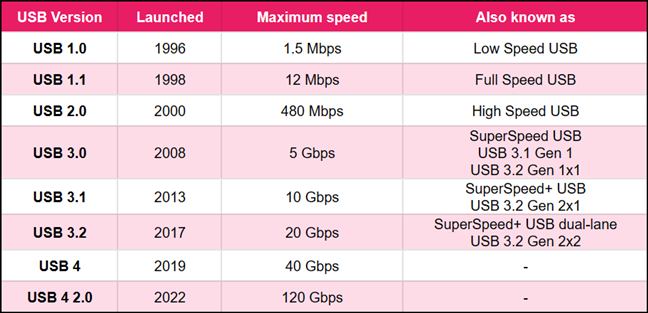
- USB 1.0 and USB 1.1 were the first iterations of the USB interface, released in 1996 and 1998, respectively, and they were capable of data transfers with speeds of up to 1.5 Mbps, respectively 12 Mbps. At the time they were developed, USB 1.0 was also known as Low Speed USB, while USB 1.1 was known as Full Speed USB.
- USB 2.0, also known as High Speed USB, was released in April 2000, and it supports maximum theoretical data transfer speeds of up to 480 Mbps. In reality, the maximum effective throughput is limited to 280 Mbps or 35 MB/s. USB 2.0 is backward compatible with USB 1.0 and USB 1.1, meaning you can use old devices with USB 1.x ports to connect to newer devices with USB 2.0 ports.
- USB 3.0 came to life in November 2008, and it’s also known as SuperSpeed USB. It can support theoretical data transfer speeds of up to 5 Gbps, but the real-life speeds you can get on it are around 3.2 Gbps or 400 MB/s. For some reason, USB 3.0 is also known as USB 3.1 Gen 1 or USB 3.2 Gen 1x1, which adds to the confusion, but that is what it is, and there’s nothing much we can do. 🙂
- USB 3.1 was released in July 2013 and is also known as SuperSpeed+ USB or USB 3.2 Gen 2x1. It is capable of theoretical data transfers of 10 Gbps, double that of USB 3.0. In reality, the maximum achievable transfer speed is 7.2 Gbps or 900 MB/s. Worth noting: this is the last USB version that’s compatible with Type A connectors (more on that later in this guide).
- USB 3.2 is also known as SuperSpeed+ USB dual-lane and is commonly referred to as USB 3.2 Gen 2x2. Launched in August 2017, it supports both one-lane and dual-lane modes, offering speeds of up to 10 and 20 Gbit/s, respectively. Furthermore, it requires the use of Type C connectors, which are mandatory from this version onwards.
- USB 4 appeared in August 2019. It allows for speeds of up to 40 Gbit/s in dual-lane mode and can tunnel DisplayPort 1.4a and PCI Express traffic using the Thunderbolt 3 protocol.
- USB 4 2.0 was announced in September 2022 and offers huge speeds of up to 120 Gbit/s.
USB types chart
Now that we’ve seen what types of USB standards there are, it’s time to take a look at the types of USB ports and connectors, too:
What types of USB ports and connectors are there?
There are many types of USB ports and connectors, and before we show you the most common, let’s first see what’s the difference between a USB port and a USB connector:
- A USB connector is the end of a USB cable that connects to a USB port.
- A USB port is a location on your computer or device into which you plug a USB connector.
Here are the most common USB connectors and ports:
USB Type A - is one of the most common types of USB connectors and ports. This type of port is found on most computers and laptops. The connector is large and bulky, found at the end of the USB cable that you will plug into your computer. USB Type A appeared together with USB Type B when the first USB specification was released, in 1996.

A USB Type-A connector
USB Type B - probably the largest USB connector out there, the USB Type B is square-shaped, with two small bevels on two of its corners. The USB Type B connector is generally used at the end of the USB cable that plugs into your printer, scanner, and other large devices.

A USB Type-B connector
Mini USB - is a smaller version of the USB Type A and USB Type B connectors. It was introduced in 2000. However, Mini USB connectors are very rare these days, as they’ve become outdated and have been replaced by Micro USB connectors.

A Mini USB connector
Micro USB - is even smaller than a Mini USB connector and is also rarely used these days. Introduced in 2007, you can still find them on some affordable smartphones and cameras.
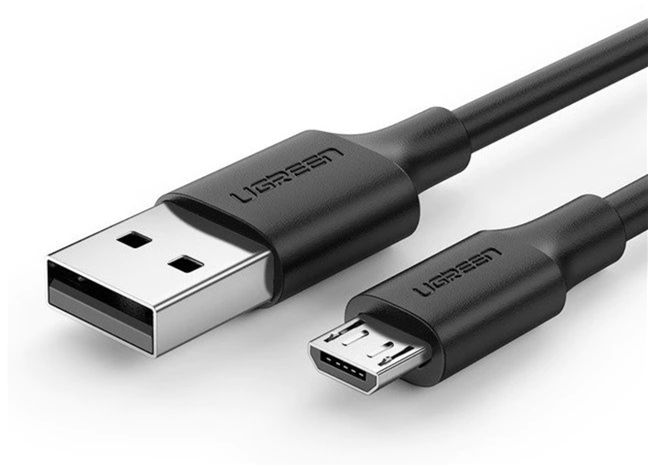

A USB Type-A to Micro USB cable
USB Type C - is the newest version of a USB connector, released in 2014, and it’s characterized by two things: it’s small and reversible. USB Type-C is commonly used for USB 3.1 ports, and all the USB versions from USB 3.2 to USB 4 and later require it!
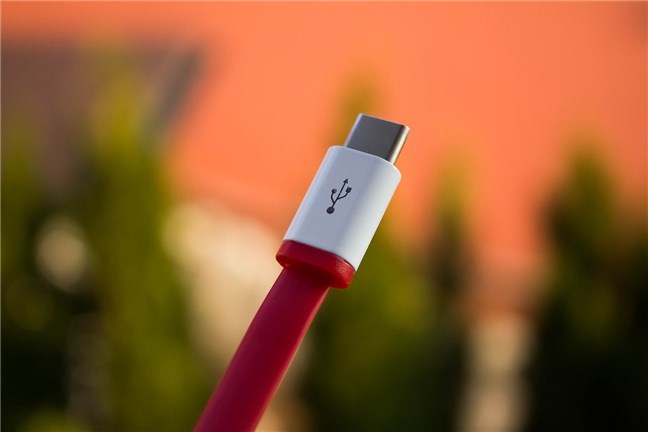

A USB Type C connector
NOTE: The USB Type C connector was created roughly at the same time the USB 3.1 was released, hence the common mistake people make in assuming that USB 3.1 and USB Type C are one and the same. In reality, they’re not, as USB 3.1 is a USB protocol, while USB Type C is a connector specification. Furthermore, to add to the confusion, there are some devices (mainly smartphones) that come with USB Type C connectors but only support USB 2.0.
Do you have any other questions about USB?
Now you have a clearer idea of what USB stands for and why it’s useful. Furthermore, you know how this standard has evolved over time and the differences between the many types of USB connectors. If you have any further questions about this subject, don’t hesitate to ask in the comments section below.


 05.05.2023
05.05.2023